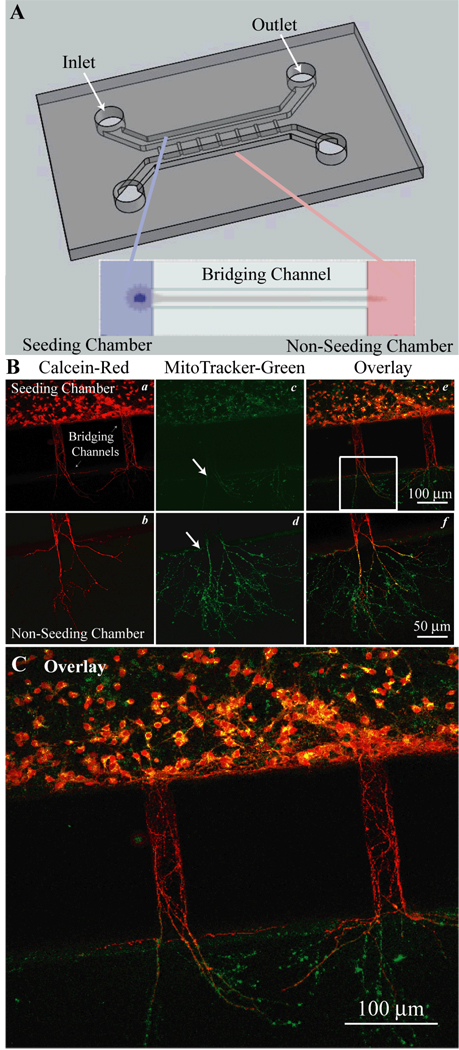
Figure 1. Cortical neuron cultures in PDMS microfluidic devices.
A. Microfluidic devices were adhered to a poly-d-lysine (PDL) coated coverslips to create a water tight, gas permeable chamber. The devices had two larger parallel chambers (0.4 mm wide, 0.25 mm tall) labeled as the seeded and non-seeded chambers. Inlet and outlet ports through the PDMS were created for cell loading and media exchange. These chambers were connected by a series of 200–300 µm long micro-bridging channels (30 µm wide, 3–5 µm tall) that exclude neuronal soma, but through which neurites can extend. Expanded view shows neuronal soma in the seeded channel with processed extending through the bridging channel into the non-seeded channel. B. Neurons cultured in the microfluidic device were imaged with calcein and MitoTracker dyes to access cell viability (a–f). C. An enlarged view of panel B (f) provides detailed information.