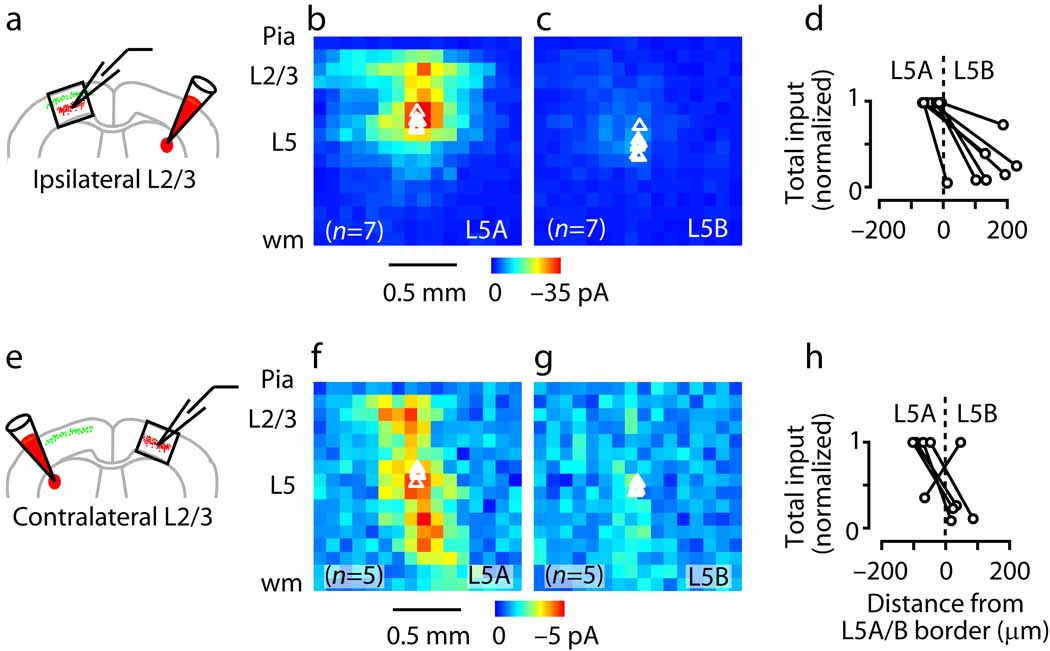
Fig. 4.
CRACM analysis of the sub-layer specificity of circuits within the class of crossed corticostriatal neurons, showing that layer 2/3 axons provide input to layer 5A but not layer 5B corticostriatal neurons. (a) CRACM analysis of ipsilateral layer 2/3 projections to corticostriatal neurons. Schematic depicts double-labeling paradigm for examining ipsilateral (local) layer 2/3 inputs to crossed corticostriatal neurons. (b) Average ipsilateral layer 2/3 input to layer 5A corticostriatal neurons. (c) Average ipsilateral input for layer 5B corticostriatal neurons (same color scale). (d) Total ipsilateral input as a function of distance from layer 5A/B border. Recordings were paired (i.e., one layer 5A and one layer 5B neuron) and values normalized to the higher value of the pair. (e) CRACM analysis of contralateral (callosal) layer 2/3 projections to crossed corticostriatal neurons. (f) Average callosal layer 2/3 input to layer 5A corticostriatal neurons. (g) Average contralateral input to layer 5B corticostriatal neurons (same color scale). (h) Total contralateral input as a function of distance from the layer 5A/B border.