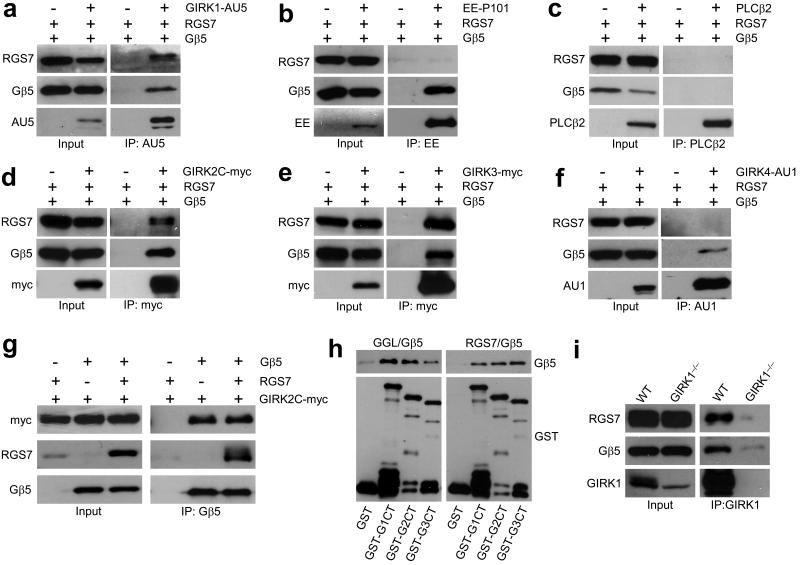
Figure 1. The Gβ5–RGS7 complex binds specifically to GIRK channels.
a–c) Co–immunoprecipitation of RGS7 and Gβ5 with GIRK1 (a) but not with P101 subunit of PI3Kγ (b) or PLCβ2 (c) from transfected 293T cells. ‘+’ and ‘−’ denote the presence and absence, respectively, of the pertinent expression construct in the transfection mixture. Immunoprecipitations (IP) were conducted with antibodies against epitope–tagged effectors (3 μg each) and resultant immunocomplexes were probed for the presence of RGS7, Gβ5, and effector by immunoblotting. Transfected cells without effector construct served as controls for non–specific binding. d–f) RGS7 and Gβ5 co–immunoprecipitate with GIRK2 and GIRK3 but not GIRK4. Tagged GIRK subunits were immunoprecipitated from cells co–transfected with RGS7 and/or Gβ5, and proteins in the eluates were detected by immunoblotting. g) GIRK2 co–immunoprecipitated with Gβ5 in the absence and presence of RGS7. h) Gβ5–RGS complexes bind to GIRK subunits via direct protein–protein interactions. GST–tagged C–terminal (ct) cytoplasmic domains of GIRK1 (GST–G1ct), GIRK2 (GST–G2ct), and GIRK3 (GST–G3ct) subunits were immobilized on beads and incubated with either purified recombinant full–length RGS7/Gβ5 (right) or Gβ5 bound to the Gγ–like (GGL) domain of RGS9 (left). Proteins retained on the beads after washing were detected by immunoblotting with anti–Gβ5 and anti–GST antibodies. i) Gβ5 and RGS7 associate with GIRK1 in the mouse hippocampus. Hippocampal membrane samples were prepared from wild–type and Girk1–/– mice and used in co–immunoprecipitation studies. Both Gβ5 and RGS7, co–immunoprecipitated with GIRK1 in wild–type but not Girk1–/– samples. Immunoblots were cropped for space reduction. Please refer to Supplemental Fig. S4 for full-length blots.