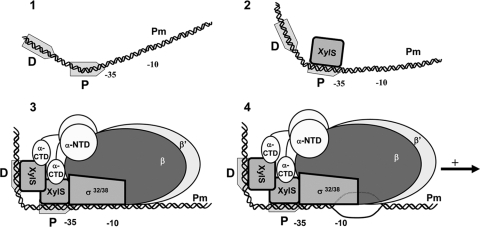
FIG. 8.
Scheme of the sequential binding model of XylS to Pm. (Step 1) Free DNA. The −10/−35 RNAP binding site and the two XylS binding sites (D, distal; and P, proximal) are depicted. The bending angle is 35°, centered in the XylS proximal binding site. (Step 2) A first XylS monomer binds Pm at the proximal site, shifts the bent center to DNA sequence between the two sites, and increases the bending angle to 50°. (Step 3) This change favors binding of a second monomer at the distal site, further increasing the DNA curvature to an overall value of 98° (here schematized as a right angle). Contacts are established with RNAP through the α-CTD and probably with the σ subunit, which as shown in step 4 favors open complex formation and transcription initiation (54).