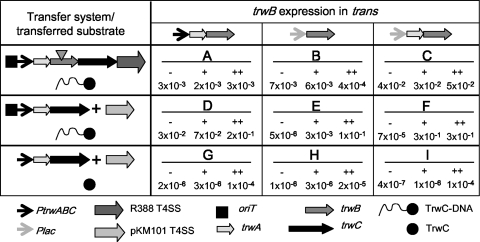
FIG. 2.
Scheme of the different conjugation assays used in this work and the transfer frequencies obtained. The elements of the transfer machinery present in each assay type (A to I) are represented as indicated in the lower part of the figure. The transposon insertion inactivating trwB in the R388 derivative is represented by a triangle. The different plasmids (separated by “+” symbols) present in the donor strains are the sum of those in the lane and column matching for each assay type; lanes also indicate the transferred product (either TrwC alone or with covalently attached DNA). Standard (A to F) or triparental (G to I) matings were performed as described in Materials and Methods. IPTG was added to the mating plate only (+) or was preceded by an additional 2-h incubation in liquid (++), as explained in Materials and Methods. Frequencies (as number of transconjugants per donor) are the mean of 3 to 5 independent experiments. Under these assay conditions, background transfer in the absence of a mobilizable plasmid is <10−7 transconjugants/donor and R388 transfer frequency is 10−1 transconjugants/donor.