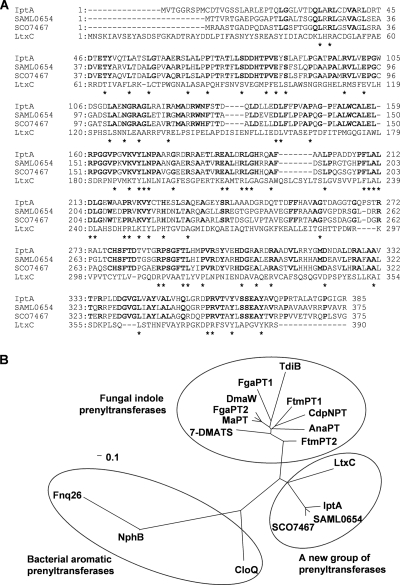
FIG. 3.
Multiple sequence alignment of IptA homologs and phylogenetic analysis of microbial prenyltransferases. (A) The amino acids conserved in all four proteins are indicated by asterisks. Dashes indicate gaps introduced for optimization of the alignment. IptA is from Streptomyces sp. SN-593 (GenBank accession no. AB512764), SAML0654 is from Streptomyces ambofaciens ATCC 23877 (CAJ89640), SCO7467 is from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) (NP_631515), and LtxC is from a cyanobacterium (AAT12285). Bold letters show the identical amino acids among IptA, SAML0654, and SCO7467. (B) Phylogenetic tree of microbial prenyltransferases. CLUSTALW (http://clustalw.ddbj.nig.ac.jp/top-j.html) was used for alignment. An unrooted phylogenetic tree was produced using the TREE VIEW program (http://taxonomy.zoology.gla.ac.uk/). The scale bar corresponds to a genetic distance of 0.1 substitution per position. The Streptomyces prenyltransferases (GenBank accession no.) used were Fnq26 (CAL34104) from Streptomyces cinnamonensis, NphB (BAE00106) from Streptomyces sp. CL 190, and CloQ (AAN65239) from Streptomyces roseochromogenes. The fungal indole prenyltransferases (GenBank accession no.) used were DmaW (Q6X2E0) from Claviceps purpurea; FtmPT1 (AAX56314), FtmPT2 (EU622826), FgaPT1 (XP_756136), FgaPT2 (AAX08549), CdpNPT (ABR14712), and 7-DMATS (ABS89001) from Aspergillus fumigatus; TdiB (ABU51603) from Aspergillus nidulans; MaPT (ABZ80612) from Malbranchea aurantiaca; and AnaPT (EAW16181) from Neosartorya fischeri.