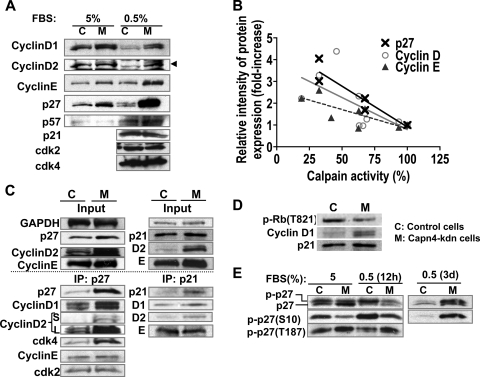
FIG. 7.
Capn4 knockdown ATDC5 cells exhibited significant accumulation of cell cycle proteins known to be calpain substrates. (A) Knockdown of Capn4 showed accumulation of cyclin D1, cyclin D2, cyclin E, and p27Kip1 in ATDC5 cells. (B) Calpain activity and relative intensity of protein expression of cyclin D, cyclin E, and p27Kip1 were negatively correlated. Three independent stable cells lines stably expressing Capn4 miRNAs, whose levels of calpain activity were approximately 30%, 65% and 90% of those of control cells were used in the experiments. (C) p27Kip1 predominantly assembled cyclin D and cdk4 rather than cyclin E and cdk2 in Capn4 knockdown ATDC5 cells. Ablation of Capn4 did not increase p21Cip1 protein levels as significantly as it did p27Kip1; however, slightly increased p21Cip1 also bound to excess cyclin D1 and cyclin D2 without altering total binding to cyclin E compared with control cells. S and L in cyclin D2 columns represent images obtained after short (S) and long (L) exposure to films. (D) Knockdown of Capn4 in ATDC5 cells showed impaired phosphorylation of Rb on T821. (E) Knockdown of Capn4 in ATDC5 cells showed impaired phosphorylation of p27Kip1 on S10 in a DMEM-F12 medium containing 5% FBS. Serum starvation for 12 h stimulated phosphorylation of p27Kip1 on S10 in both control and Capn4 knockdown cells. Serum starvation for 3 days caused significant accumulation of phospho-p27Kip1 (S10) in Capn4 knockdown ATDC5 cells.