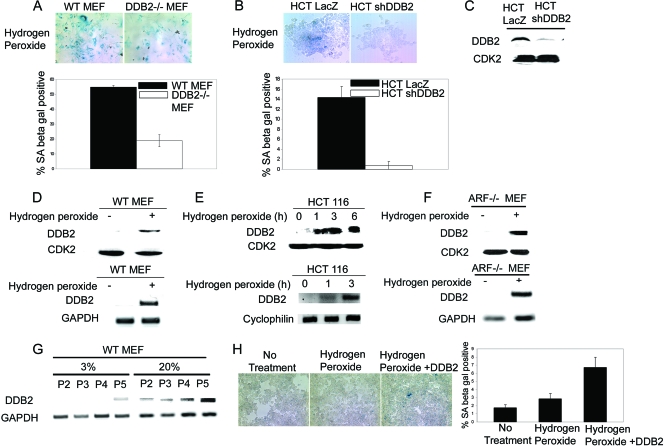
FIG. 3.
DDB2-deficient cells are resistant to oxidative stress-induced senescence. (A) WT or DDB2−/− MEFs were treated with 150 μM hydrogen peroxide for 4 h. After 3 days, cells were analyzed for the SA-β-Gal activity. (Top) Representative images of WT and DDB2−/− MEFs stained for SA-β-Gal after hydrogen peroxide treatment. (Bottom) SA-β-Gal-positive cells were counted from at least 10 fields of triplicate plates. (B) HCT116 cells expressing LacZ shRNA or DDB2 shRNA were treated with 150 μM hydrogen peroxide for 4 h. After 3 days, cells were analyzed for SA-β-Gal activity. (Top) Representative images of HCT116 cells expressing LacZ shRNA or DDB2 shRNA stained for SA-β-Gal after hydrogen peroxide treatment. (Bottom) SA-β-Gal-positive cells were counted from at least 10 fields of triplicate plates. (C) HCT116 cells expressing LacZ shRNA or DDB2 shRNA were analyzed for the level of DDB2 expression. (D and E) WT MEFs or HCT116 cells were treated with 150 μM hydrogen peroxide for 4 h or the indicated time points. (Top) Extract of the cells was analyzed for the level of DDB2 by Western blotting. (Bottom) Total RNA was analyzed by semiquantitative PCR for the level of DDB2. (F) ARF−/− MEFs were treated with 150 μM hydrogen peroxide for 4 h. (Top) Extract of the cells was analyzed for the level of DDB2 by Western blotting. (Bottom) Total RNA was analyzed by semiquantitative PCR for the level of DDB2. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (G) WT MEFs were maintained in the culture medium either in 3% oxygen or in 20% oxygen up to passage 5. Total RNA for each passage was analyzed by semiquantitative PCR for the level of DDB2. (H) HCT116 cells expressing DDB2 shRNA cells were transfected with DDB2. On the next day, transfected or nontransfected cells were treated with 150 μM hydrogen peroxide for 4 h followed by change of medium. After 36 h cells were stained for SA-β-Gal expression.