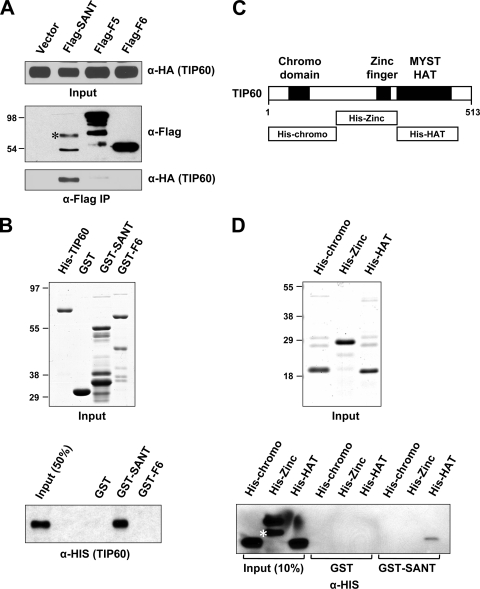
FIG. 3.
Identification of the TIP60 HAT domain as a direct target of the p400 SANT domain. (A) Association of TIP60 with the p400 SANT domain in 293T cells. HA-TIP60 was coexpressed with Flag-p400 fragments (indicated at the top), and proteins bound to M2 agarose (anti-Flag immunoprecipitation) were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-Flag and anti-HA antibodies. A nonspecific immunoblot signal is marked by an asterisk. (B) Direct binding of TIP60 to the p400 SANT domain. Recombinant His-tagged TIP60 and GST-p400 fragments were expressed in E. coli cells; purified through Ni-nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) and glutathione-Sepharose 4B resins, respectively; analyzed by SDS-PAGE with Coomassie staining (top); and used in GST pulldown assays (bottom). His-TIP60 binding to GST or GST fusion proteins was scored by immunoblotting with an anti-His antibody. (C) Schematic representation of TIP60. Three TIP60 fragments corresponding to the chromodomain, the zinc finger, and the HAT domain are shown. (D) Binding of TIP60 fragments to the p400 SANT domain. The TIP60 fragments shown in C were purified from E. coli cells, analyzed by SDS-PAGE with Coomassie staining (top), and used in GST pulldown assays (bottom). TIP60 binding to GST-SANT was detected by immunoblotting with an anti-His antibody. A degraded His-chromodomain is indicated by an asterisk.