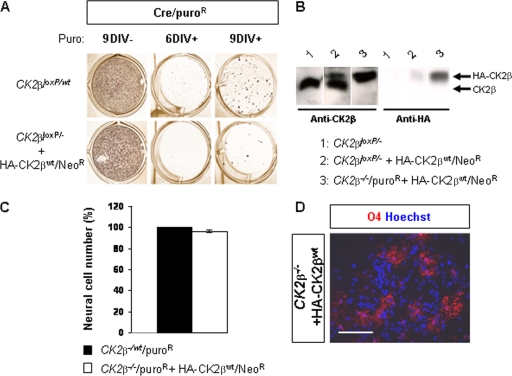
FIG. 7.
Exogenous CK2β expression in NSC-derived CK2β−/− embryonic stem (ES) cells promotes proliferation and oligodendroglial differentiation. (A) Clonal selection of CK2β−/−, Cre-pMSCV-puro-cultured (Cre/puroR) ES cells expressing exogenous HA-CK2βwt/Neor protein. CK2β−/wt, Cre/puroR ES cell clones were generated in parallel and served as positive controls. (B) Western blot analysis with anti-CK2β (left panel) and anti-HA (right panel) antibodies of CK2βloxP/− ES cells, CK2βloxP/− and HA-CK2βwt/Neor ES cells, and CK2β−/−, Cre/puroR, and HA-CK2βwt/Neor ES cells. Note the complete absence of the endogenous CK2β protein in the CK2β−/− ES cell extract. (C) Proliferation analysis of NSC-derived ES cells. The ratio (percentage) of the number of cells present in neurosphere-derived CK2β−/− ES cells expressing the exogenous HA-CK2βwt protein to the number of cells present in control neurosphere-derived CK2β−/wt ES cells was unchanged when normalized to the CK2β−/wt ES cell line (7 differentiation cultures). (D) O4+ differentiating OPCs were identified from neurosphere-derived CK2β−/− ES cells expressing the exogenous HA-CK2βwt protein and allowed to differentiate. Scale bar, 100 μm.