FIG. 1.
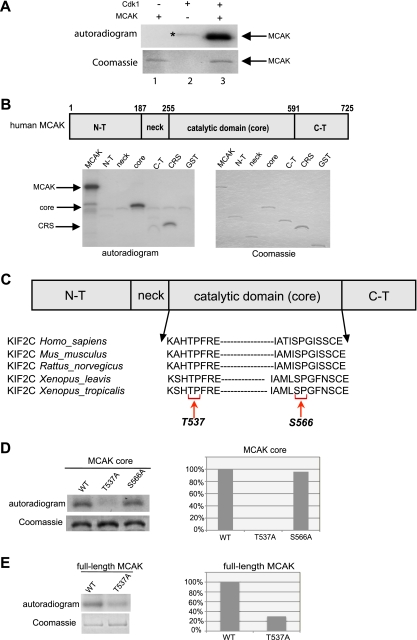
Cdk1 phosphorylates T537 in the core domain of MCAK. (A) Purified His6-tagged MCAK was subjected to kinase assays in vitro with active Cdk1/cyclin B1 (upper panel). *, autophosphorylated GST-cyclin B1. (B) (Upper panel) Schematic illustration of various domains of MCAK. (Lower panels) Kinase assays in vitro of GST-tagged MCAK domains with Cdk1/cyclin B1 (left panel). Cytoplasm retention signals (CRS) of cyclin B1 and GST proteins were taken as positive and negative controls, respectively. The same gel was stained with Coomassie blue as an input control (right panel). N-T, N terminus; C-T, C terminus. (C) Alignment of T537 and S566 in the catalytic core domain of MCAK in various species. (D) Kinase assays were performed using the GST-tagged core domain of MCAK and its mutants T537A and S566A, and the same gel was stained with Coomassie blue as an input control (left panel). Quantification of phospho-intensity, relative to the level for the input control (right panel). (E) Kinase assays of GST-tagged full-length MCAK, its mutant MCAK T537A, and the Coomassie blue staining control (left panel). Quantification of phospho-intensity, relative to the level for the input control (right panel).