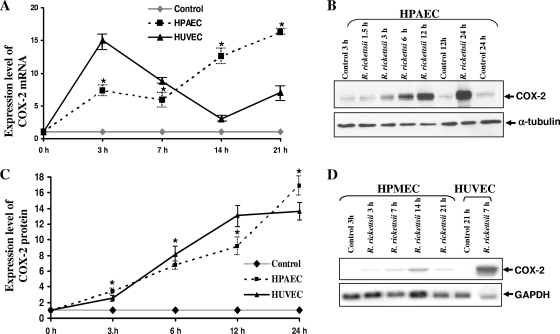
FIG. 5.
Increased expression of COX-2 mRNA and protein synthesis in macrovascular ECs infected with R. rickettsii. Panel A depicts densitometric analysis of changes in steady-state levels of COX-2 transcriptional activation in HPAECs and HUVECs after R. rickettsii infection. The results are presented as the mean fold induction over the basal level ± SE (n ≥ 3). The asterisks indicate statistically significant differences in COX-2 mRNA expression relative to the baseline in uninfected controls. Panel B shows the results of a typical Western blot with uninfected (Control) and R. rickettsii-infected HPAECs. Total protein lysates of HPAECs infected for 1.5 to 24 h or incubated with medium alone (Control) were analyzed by Western blotting to determine the steady-state levels of cellular COX-2 protein. Blots were probed in succession with anti-human COX-2-specific antibody and an anti-α-tubulin antibody. Densitometric analysis of changes in COX-2 protein levels in HPAECs and HUVECs infected with R. rickettsii was then performed (C). The data are presented as the mean fold induction ± standard error over the baseline value of 1 (n ≥ 3). Panel D shows a representative Northern blot for the detection of basal and R. rickettsii-induced COX-2 expression in HPMECs infected for different lengths of time. HUVECs infected with R. rickettsii for 7 h were included as a positive control in this experiment.