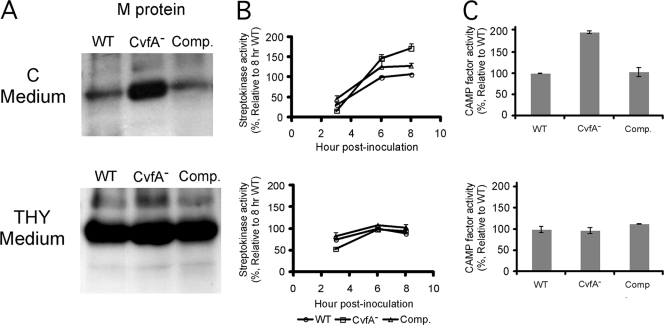
FIG. 4.
Biochemical assay to confirm the results of transcript analysis. The wild-type (WT) strain (HSC5spc), CvfA− mutant strain (ΩCvfA strain), and CvfA− complemented strain (Comp.) (ΩCvfA::pCIV2:: cvfA) were used. The CvfA− mutant exhibits a phenotype different from that of the wild type only in C medium, not in THY medium. (A) Western blot against M protein. The amounts of M protein in cell wall fractions were compared by Western blotting. The cysteine protease inhibitor E-64 (final concentration, 10 μM) was added to S. pyogenes culture to prevent the degradation of M protein by SpeB. (B) Streptokinase activity. The activities of streptokinase in the supernatants of cultures 3, 6, and 8 h postinoculation were analyzed and expressed relative to the activity in supernatant of the wild-type culture 8 h postinoculation. The data are the means and standard errors of the means derived from at least three independent experiments. The cysteine protease inhibitor E-64 (final concentration, 10 μM) was added to S. pyogenes culture to prevent the degradation of streptokinase by SpeB. (C) CAMP test. CAMP factor activity was measured by streaking S. pyogenes strains perpendicular to a streak of S. aureus producing β-toxin on agar plates containing C medium or THY medium and 5% (vol/vol) sheep blood. CAMP factor activity was expressed relative to the activity of the wild type. The CAMP factor activities were compared by measuring the area of CAMP hemolysis zone using ImageJ software (NIH) after the plates were scanned. The data are the means and standard errors of the means derived from at least two independent experiments.