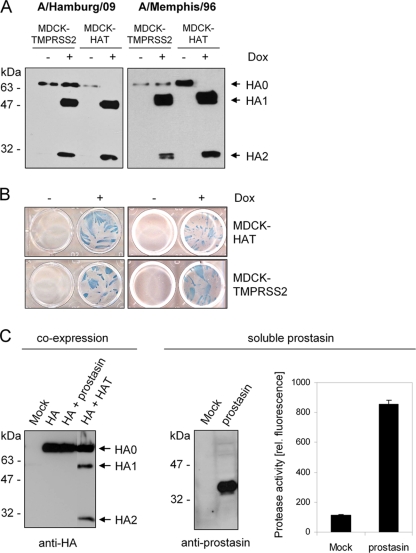
FIG. 2.
Proteolytic processing of HA by the proteases HAT, TMPRSS2, and prostasin. (A) MDCK-TMPRSS2 and MDCK-HAT cells were infected with H1N1 influenza viruses A/Hamburg/09 or A/Memphis/96 at an MOI of 0.01 and incubated in the absence (−) or presence (+) of doxycycline (Dox) for 24 h. Virus-containing cell supernatants were concentrated by ultracentrifugation, subjected to SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, and subsequently transferred to a PVDF membrane and analyzed by using HA-specific antibodies and HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies. (B) MDCK-HAT and MDCK-TMPRSS2 cells were infected with A/Memphis/96 or A/Hamburg/09 at an MOI of 0.01 and incubated in the absence or presence of Dox for 24 h to allow multiple cycles of viral replication. Infected cells were immunostained against the viral nucleoprotein. (C) MDCK cells were cotransfected with pCAGGS-HA and either pCAGGS, pCAGGS-prostasin, or pCAGGS-HAT. Mock transfections were done with empty pCAGGS. At 24 h posttransfection, cell lysates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with antibodies against H3 (left panel). Supernatants of pCAGGS-prostasin or pCAGGS (Mock) transfected MDCK cells were concentrated ∼100-fold and subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis with prostasin-specific antibodies (middle panel). Enzymatic activity of the supernatants was examined by incubation with the fluorogenic substrate peptide Boc-Leu-Gly-Arg-AMC and release of AMC due to hydrolysis of the substrate was measured. The results are presented as mean enzymatic activities for three independent experiments.