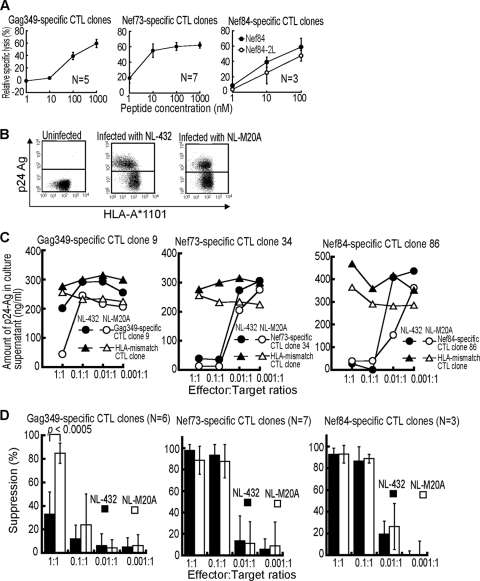
FIG. 2.
Ability of HLA-A*1101-restricted CTLs to suppress HIV-1 replication in HIV-1-infected CD4+ T cells. (A) Cytolytic activities of HLA-A*1101-restricted HIV-1-specific CTLs (5 Gag349-specific, 7 Nef73-specific, and 3 Nef84 consensus B-specific CTL clones) were tested by using C1R-A*1101 cells pulsed with various concentrations of the corresponding peptide (effector-to-target-cell ratio = 2:1). (B) Surface expression of HLA class I molecules on CD4+ T cells infected with HIV-1 NL-432 or NL-M20A. CD4+ T cells infected with HIV-1 NL-432 or NL-M20A were stained with anti-HLA-A*1101 and anti-p24 MAbs and then analyzed by using flow cytometry. (C) Ability of HLA-A*1101-restricted CTLs to suppress HIV-1 replication in cultures of HIV-1-infected CD4+ T cells. CD4+ T cells from an HLA-A*1101+ healthy individal were infected with NL-432 or NL-M20A and then cocultured with HLA-A*1101-restricted CTL clones or HLA-mismatch CTL clone (HLA-B*5101) at various effector-to-target ratios. HIV-1 p24 Ags in the supernatant were measured on day 6 or 7 postinfection by conducting an enzyme immunoassay. (D) Analysis using multiple HLA-A*1101-restricted CTLs to suppress replication of NL-432 or NL-M20A.