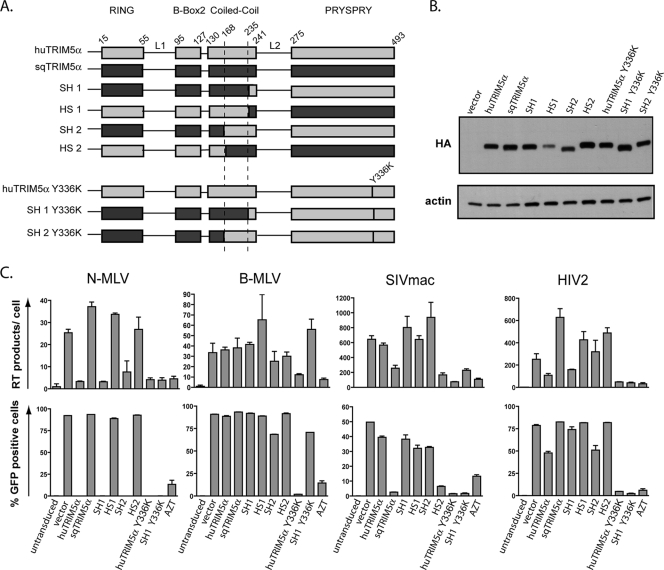
FIG. 1.
The TRIM5α RBCC influences the specificity of retroviral restriction. (A) Schematic representation of squirrel monkey (sqTRIM5α) and either human wild-type TRIM5α (huTRIM5α) or Y336K mutant (huTRIM5α Y336K), and of the derived chimeras. The four domains (RING, B-Box2, coiled-coil, and PRYSPRY) with the linker regions 1 and 2 (L1 and L2) are depicted. The numbering of positions delimiting the domains is based on the human TRIM5α sequence. (B) Western blot analysis of extracts from MDTF cells stably transduced with a retroviral control vector (vector) or with vectors expressing HA-tagged versions of TRIM5α and derivatives, using HA (top)- and actin (bottom)-specific antibodies. (C) MDTF cell lines expressing the indicated TRIM5α molecules or transduced with a control vector (vector) were challenged in duplicate with a single dose of MLV, SIVmac, HIV2-, and HIV1-based GFP vectors initially titered on permissive MDTF cells, using infection of empty vector-transduced cells in the presence of azidothymidine (AZT) as a negative control. Levels of intermediate minus-strand DNA RT products were detected by real-time PCR 8 h postinfection (top), while infectivity was scored 3 days after infection by flow cytometry (bottom). The chimera HS1 restricts SIVmac only weakly, a phenotype probably caused by its low steady-state level of expression. These results are representatives of two independent experiments.