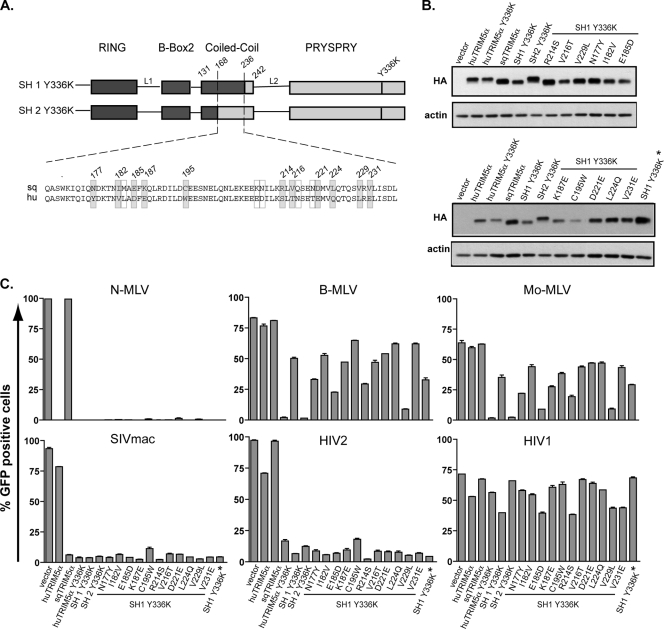
FIG. 4.
Positions 186, 214, and 229 of the CC domain condition TRIM5α specificity. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment of the region encompassing positions 168 to 236 derived from squirrel monkey (sq) and human (hu) TRIM5α. Differences are framed, with residues targeted by site-directed mutagenesis in gray. Numbering is based on the sqTRIM5α sequence. (B) MDTF cell lines stably expressing indicated HA-tagged TRIM5α derivatives were engineered by retroviral transduction and analyzed by Western blotting. Here, the cell line “SH1 Y336K*” was included in this experiment to show that there is only a minor increase in restriction despite the high overexpression of this TRIM5α chimera. (C) These cells were transduced in duplicate with N-MLV-, B-MLV-, Mo-MLV-, SIVmac-, HIV2-, or HIV1-derived GFP expressing vectors, scoring infectivity 3 days later by flow cytometry. The restriction activities from the relevant point mutants were reproduced in two independent experiments.