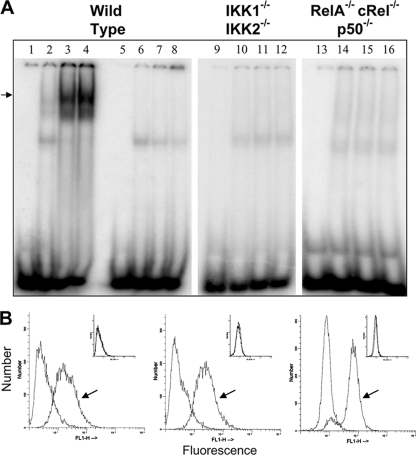
FIG. 1.
Nuclear translocation of NF-κB in JEV-infected MEFs. (A) EMSA was performed using uninfected and JEV-infected wild-type, IKK1−/− IKK2−/−, and RelA−/− cRel−/− p50−/− MEFs as indicated on top. Lanes 1 to 4 represent EMSA performed with NF-κB-specific oligomer, while lanes 5 to 8 represent EMSA performed with NF-κB mutant oligomer. Lanes 1, 5, 9, and 13 represent the oligomer alone; lanes 2, 6, 10, and 14 represent uninfected MEFs; and lanes 3, 7, 11, and 15 represent cells at 10 h p.i., while lanes 4, 8, 12, and 16 represent cells that were infected for 14 h. The arrow indicates the specific NF-κB-DNA complex. (B) As labeled in panel A, wild-type, IKK1−/− IKK2−/−, and RelA−/− cRel−/− p50−/− MEFs that were infected with JEV for 12 h were stained for the expression of intracellular JEV antigen. The arrow indicates staining with primary antiflavivirus group-specific MAb followed by fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) anti-mouse secondary antibody, while the unmarked histogram indicates staining with secondary antibody alone. The two histograms overlap in the insets, which represent staining of uninfected cells.