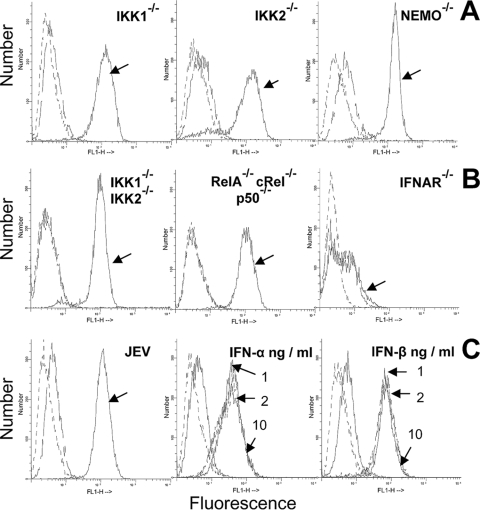
FIG. 6.
Cell surface expression of classical MHC-I (H-2b) antigens. (A) Flow cytometric analysis of H-2b expression on control and JEV-infected IKK1−/−, IKK2−/−, and NEMO−/− MEFs at 36 h after infection. (B) H-2b expression on control and IKK1−/− IKK2−/−, RelA−/− cRel−/− p50−/−, and IFNAR−/− MEFs that were infected with JEV for 36 h. (C) H-2b expression on uninfected and infected wild-type cells at 36 h p.i. is shown at left. Staining with primary (anti-H-2b specific MAb) and fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) anti-mouse secondary antibody is indicated by arrows for infected cells and by unmarked broken lines for uninfected cells, while dashed lines indicate staining with secondary antibody alone. Figures in the middle (IFN-α) and right (IFN-β) of the panel represent H-2b expression on wild-type MEFs treated for 36 h with 1, 2, and 10 ng/ml of either IFN-α or IFN-β, respectively, as indicated by arrows. The same standard IFNs obtained for ELISA measurements were used. In all histograms, dashed lines represent staining with FITC-conjugated secondary antibody alone, while H-2b expression is indicated by unmarked lines in untreated cells and arrow marks in treated/uninfected cells.