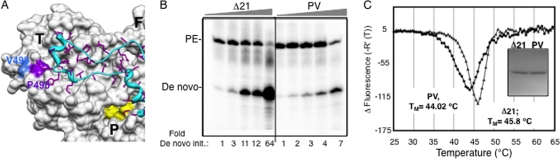
FIG. 6.
The allosteric GTP binding site and de novo initiation of RNA synthesis. (A) The location of the low-affinity GTP binding site on the surface of the thumb domain of HCV RdRp (PDB identifier 1QUV) as shown by Bressanelli et al. (6). T, F, and P, thumb, finger, and palm domains, respectively. The Δ1 loop is in cyan, and the residues P495 and V499, which were shown to bind GTP on the thumb domain, are shown in different colors. The side chains of S29 and R32, which are located in the Δ1 loop, are not highlighted, while the surfaces of P495 and V499 are in purple and blue, respectively, as indicated. Residue R503, which is part of the putative allosteric pocket, is also not highlighted. (B) Gel image of the RdRp reaction products using LE19P and PE46 with increasing protein concentrations. The two proteins were at 20, 30, 40, 50, and 120 nM in the assays. The amounts of de novo-initiated product at different enzyme concentrations were normalized and compared to that of a 20 nM concentration of either the PV mutant or Δ21, as indicated below respective lanes. PE, primer extension. (C) DSF analysis of Δ21 and PV mutant as for Fig. 4D to examine conformational differences between the two proteins. The inset shows SDS-PAGE of the two proteins used.