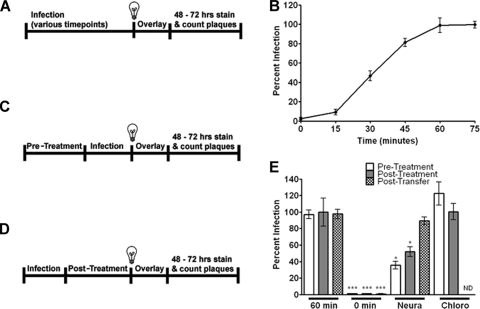
FIG. 2.
Neutral red (NR) infectious center assay confirms a pH-independent and sialic acid-dependent entry mechanism for MNV-1. (A, C, and D) Flow charts of the NR assay describing different treatment conditions. (A and B) MNV-1 rapidly becomes insensitive to light exposure. RAW 264.7 cells were infected with NR-containing virus at an MOI of 0.001, rocked at room temperature, exposed to light at 0, 15, 30, 45, 60, and 75 min postinfection (pi), and overlaid with agarose, and plaques were counted 48 to 72 h pi. (C, D, and E) MNV-1 entry is sialic acid dependent and pH independent. (C and E, pretreatment) RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated with 2.5 mU/ml Vibrio cholerae neuraminidase (Neura) or 200 μM chloroquine (Chloro) for 30 min, infected by rocking for 60 min, and overlaid with media containing agarose, and plaques were counted 48 to 72 h pi. (D and E, posttreatment) Alternatively, RAW 264.7 cells were infected with an MOI of 0.001 for 60 min and then posttreated with 2.5 mU/ml Vibrio cholerae neuraminidase (Neura) or 200 μM chloroquine (Chloro) for a total of 90 min before performing the NR assay. (E, posttransfer) In case of Vibrio cholerae neuraminidase treatment, RAW 264.7 cells were posttreated as described, scraped, and transferred to an untreated monolayer before a plaque assay was performed and viral titers were determined. *, P < 0.05.