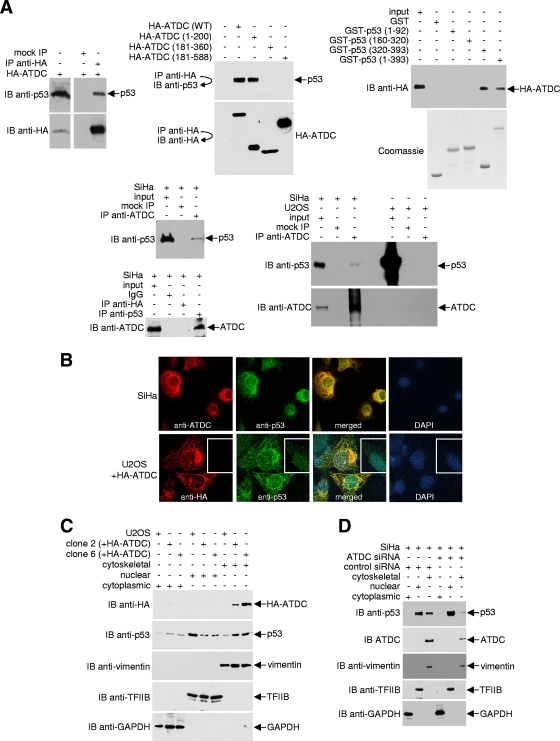
FIG. 2.
ATDC binds p53 and alters p53 subcellular localization. (A) For the top left and middle panels, 293T cells were transfected with either the pcDNA3.1HA vector or plasmids encoding the indicated HA-tagged ATDC proteins. Anti-HA immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-p53 or anti-HA antibodies. For the top right panels, GST, GST-p53, and GST-p53 deletion mutants coupled to Sepharose beads were incubated with 293T whole-cell extracts expressing HA-ATDC. After the beads were washed, bound proteins were eluted and analyzed by Western blotting with an anti-HA antibody. Samples of purified GST and GST fusion proteins were resolved on a separate gel and stained with Coomassie blue to confirm approximately equal quantities of proteins in each reaction. For the bottom panels, endogenous ATDC or p53 from extracts prepared from SiHa or U2OS cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-ADTC or anti-p53 antibodies. Immune complexes were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-p53 or anti-ATDC antibody. (B) Representative pictures of SiHa cells and U2OS cells transfected with the pcDNA3.1HA vector or transiently or stably expressing HA-ATDC, fixed, stained with antibodies or DAPI, and analyzed by confocal microscopy. (C and D) Using a compartmental protein extraction kit (Millipore) (46), cytoskeletal, nuclear, and cytoplasmic extracts were prepared from DSP-treated U2OS cells transfected with the pcDNA3.1HA vector or stably expressing HA-ATDC or from SiHa cells treated with or without ATDC siRNA. An aliquot of each fraction was subjected to Western blot analysis with either anti-HA or anti-p53 antibodies. The blot was sequentially stripped and reprobed with the indicated antibodies to assess p53 or ATDC localization and the purity of fractionation.