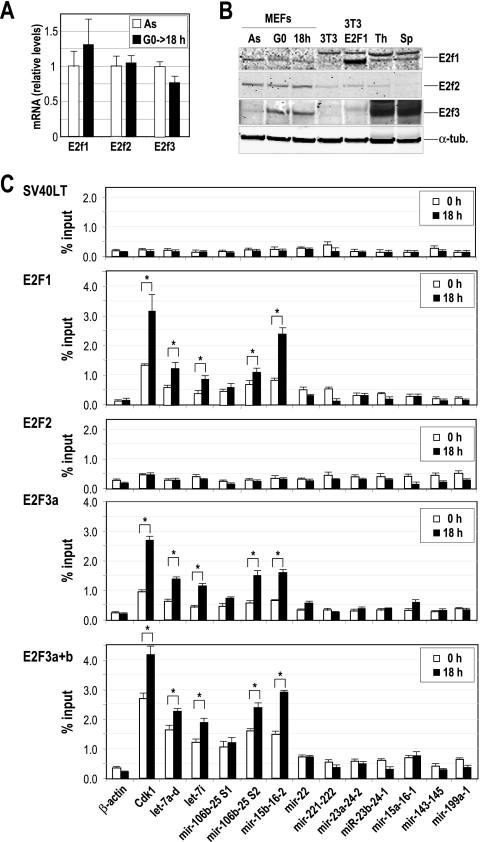
FIG. 4.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation of E2F transcription factors. (A) The relative expression of E2F factors is analyzed in primary MEFs by real-time PCR in asynchronously growing cells (As) or 18 h after serum stimulation of starved cells (G0→18 h). The mRNA levels were normalized versus the levels of GAPDH, and the mRNA level of E2F1 in As was considered to be 1. (B) Immunodetection of E2F1, E2F2, and E2F3 in As, serum-starved MEFs (G0) or G1/S primary MEFs (18 h after cell cycle entry). NIH 3T3 cells transfected with E2F1-expressing vectors or the parental cells were also used as a control. Thymus (Th) and spleens (Sp) from normal mice were also used as controls. α-Tubulin (α-tub.) was used as a loading control. (C) E2F1, E2F2, and E2F3 were immunoprecipitated from MEF protein lysates, and the predicted E2F binding sites of several miRNA clusters (dotted lines in Fig. 3) were amplified at t equals 0 h (serum starved) or 18 h after stimulation with serum. The promoter of Cdk1 was used as a positive control, whereas the β-actin promoter was used as a negative control. An unrelated antibody against the SV40 large T antigen (SV40LT) was used as a control for the IgG background at the specific miRNA promoters. Asterisks indicate significant differences (P < 0.01).