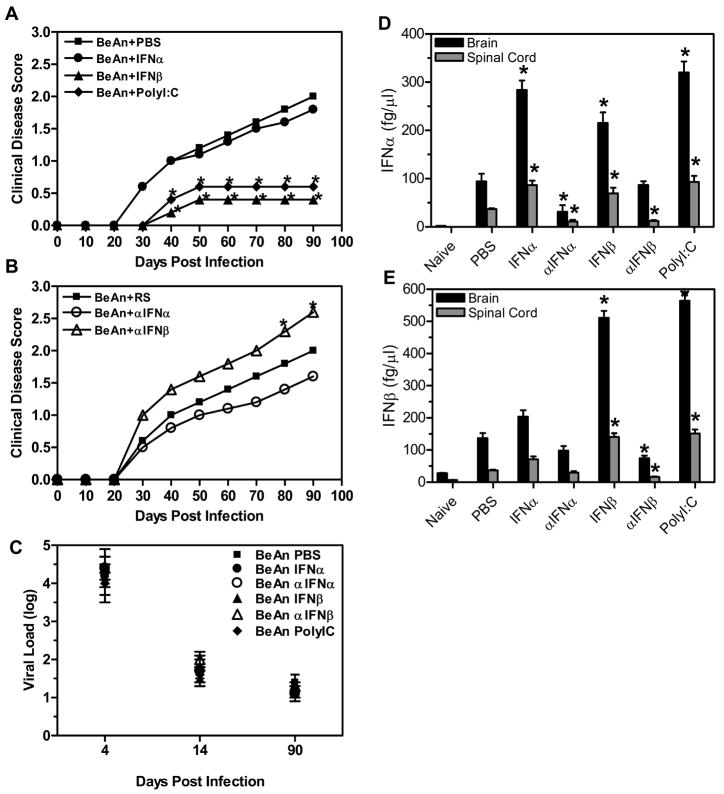
Figure 1. The innate immune response affects development of demyelinating disease.
SJL mice were infected with TMEV and administered IFNα, IFNβ, polyI:C, or PBS (A) (10 mice per group) on the day of infection and four days post infection. The mice were followed for clinical signs of demyelinating disease for 90 days following infection, PBS (square), IFNα (circle), IFNβ (triangle), and polyI:C (diamond). The stars above the line represent a statistically significant difference in the clinical score compared to TMEV- infected mice treated with PBS. TMEV- infected mice were administered antiserum to IFNα or IFNβ or rabbit serum (RS) (B) (10 mice per group) on the day of infection and four days post infection. Mice were followed for clinical signs of demyelinating disease for 90 days following infection, RS (square), αIFNα (open circle), andαIFNβ (open triangle). The stars above the line represent a significant difference in clinical disease score compared to TMEV- infected mice administered RS. (C) The brain and spinal cord were removed from TMEV- infected mice (3 per group) on 4, 14, and 90 days post infection and plaque assays were conducted to determine viral load. Viral load is the log of plaque forming units per milligram of tissue. The experiment was repeated five times with one representative experiment shown. (D, E) The brain and spinal cord were removed from mice (3 mice per group) at 7 days post infection, and RNA was isolated from the organs and converted to cDNA. Real time PCR was conducted on the cDNA using primers for IFNα (D) or IFNβ (E). The concentration for each primer was based on a standard curve with cDNA of known concentration. The experiment was repeated three times with a representative of one of the experiments shown in the graph. The stars above the bars indicate a significant difference (>3 fold increase or decrease) in expression based on the expression of control treated mice.