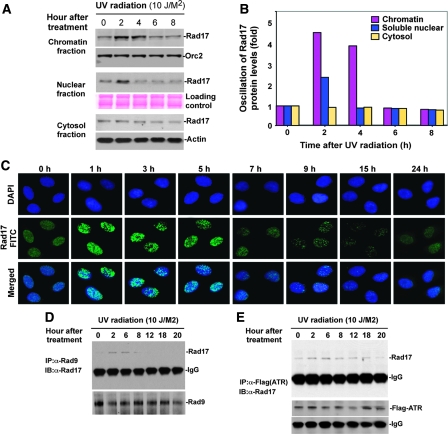
Figure 3.
Proteolytic regulation of Rad17 is associated with chromatin-based DNA damage response and dissociation of checkpoint complex. (A) UV-induced Rad17 translocation and its degradation on chromatin. HNF cells were treated with UV and harvested at indicated time points. Cell pellets were fractionated into cytosol, soluble nuclear and chromatin-enriched portions. UV-induced Rad17 degradation was examined for different cellular compartments. Normalized protein loading for chromatin, nuclear and cytosol fractions was measured by ORC2, Ponceau S staining and actin, respectively. (B) Summary of UV-induced Rad17 alterations in different cellular compartment. (C) Transient formation of Rad17 nuclear foci in response to UV radiation. HNF cells were treated with UV and fixed at the different time points followed by immunostaining with antibody against Rad17. (D) Kinetics of interaction of Rad17 and 9-1-1 induced by DNA damage is regulated by Rad17 proteolysis. HNF cells were exposed to UV and collected at the indicated time points. Endogenous Rad9 complexes were immunoprecipitated with anti-Rad9 antibody (polyclonal). Rad9 IP complex was then immunoblotted with antibody against Rad17. Co-IP Rad9 was determined by immunoblotting using antibody (monoclonal) against Rad9. (E) Kinetics of interaction of Rad17 and ATR in response to DNA damage. Flag-tagged ATR was transfected into HNF cells. Ectopically expressed Flag-ATR was immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag antibody. ATR IP complexes were immunoblotted with Rad17 antibody. Co-IP Flag-ATR was measured by immunoblotting using antibody against Flag.