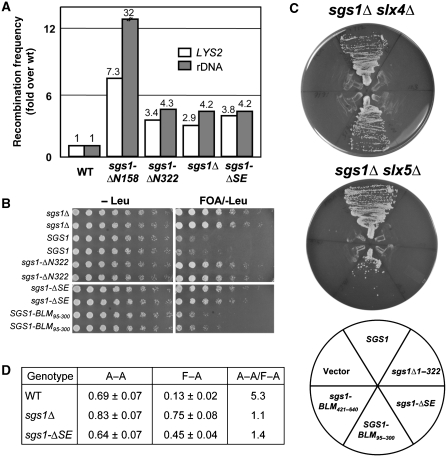
Figure 7.
The SE domain is required for multiple SGS1 functions. (A) Yeast strains of the indicated genotype were assayed for excision recombination at the LYS2 and rDNA loci as described earlier (Mullen et al, 2000). Recombination frequencies were determined and are presented as fold increase over WT. (B) Strain NJY728 (sgs1Δ top3Δ plus pJM555 (TOP3/URA3/ADE3/CEN)) was transformed with the indicated SGS1 alleles in pRS415 (LEU2/CEN). Transformants were streak purified on SD-leu plates, resuspended to OD600=3.0 and serially diluted in five-fold increments. Approximately 5 μl were spotted onto SD plates lacking leucine but with or without 5-FOA. Plates were photographed after 2 (−Leu) or 5 (5-FOA/−Leu) days growth at 30°C. (C) Strains NJY2083 (sgs1–11∷loxP slx4–11∷loxP plus pJM500 (SGS1/URA3/ADE3/CEN)) and NJY602 (sgs1–11∷KAN slx5-10∷TRP1 plus pJM500) were transformed with various SGS1 alleles in pRS415 as indicated in the key. Transformants were streaked onto plates containing 5-FOA and the plates were photographed after 2 (sgs1Δ slx4Δ) or 3 (sgs1Δ slx5Δ) days growth at 30°C. (D) Cells of the indicated genotype were assayed for viability after inducing HO endonuclease in SSA reporter strains that contained either homologous (A-A) or homeologous (F-A) direct repeats flanking the HO cut site (Sugawara et al, 2004). Results shown are the average viability±s.d.