Figure 3.
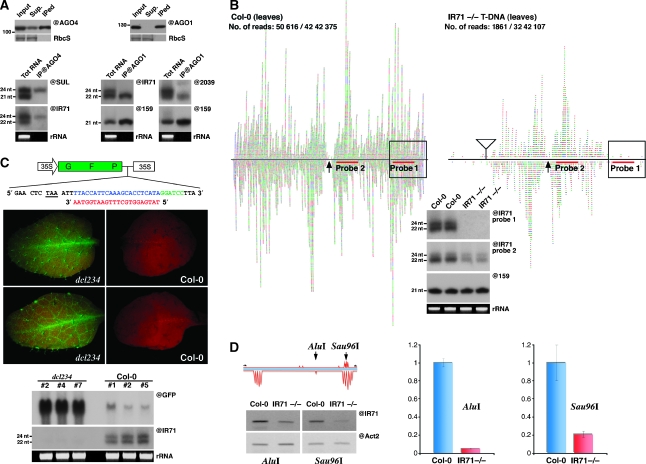
IR-derived siRNAs are loaded into cognate AGO proteins and can function at both post-transcriptional gene silencing and RNA-directed DNA methylation levels. (A) Immunoprecipitation experiments were conducted using either an AGO4- or AGO1-specific antibody. The presence of either AGO1 or AGO4 in each IP was confirmed by protein blot analysis (upper panels). Total RNA extracted from the respective IPs was subjected to northern analysis using the indicated probes. (B) Sequencing and molecular confirmation of siRNAs from Col-0 and a T-DNA insertion line at the IR71 locus. siRNAs sequenced from the aforementioned genotypes, including the predicted terminal loop (arrow), the number of IR71 reads compared with the total number of reads and the location of probes used in the gel blot analysis. Also shown is the location of the T-DNA insertion (triangle), with the boxed region representing the predicted region of the IR fold-back structure that would be disrupted by the insertion. (C) A schematic representation of the 35S:GFP sensor used to assay the post-transcriptional silencing ability of AGO1-loaded IR71-derived siRNAs. A recognition sequence (blue) for the highly AGO1-loaded siRNA (red) was inserted three bases after the stop codon of GFP at the start of the 3′UTR. The middle panels show the GFP sensor fluorescence after transformation into either a dcl2/dcl3/dcl4 triple mutant (left) or Col-0 plant (right). Northern blot analysis (bottom panel) confirms the strong GFP mRNA decrease and the presence of IR71-derived siRNAs in silenced Col-0 plants, and the converse for non-silenced dcl2/dcl3/dcl4 plants. (D) Analysis of DNA methylation induced by IR71-derived siRNAs. A schematic representation of the predicted regions of methylation within a 300-nt portion of the IR71 fold-back disrupted by the T-DNA insertion, including the location of the primer and restriction sites used. sqPCR analysis (@IR71) of DNA extracted from the indicated genotypes after digestion with the methylation-sensitive enzyme AluI or Sau96I. Equal input of DNA was confirmed by amplification of a region of actin-2 (@Act2) lacking either restriction site. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis (right) confirmed the results of the semi-quantitative approach.