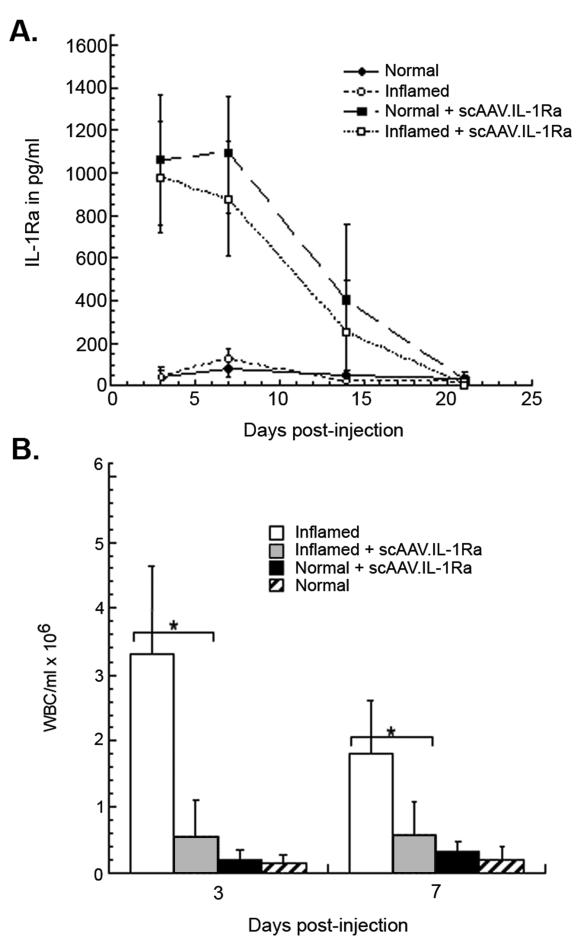
Figure 3.
Intra-articular expression of scAAV.IL-1Ra after direct injection into normal and inflamed rabbit knee joints. Ten rabbits were initially injected in both knees with 5 × 104 HIG-82-IL-1β-neo cells, which stimulates an immediate, persistent inflammatory state. Three days later, 5 × 1011 particles of scAAV.IL-1Ra were injected into both knees of five of the rabbits with inflamed knees and five normal rabbits. An equivalent volume of saline was injected into the remaining five inflamed rabbits and an additional five normal rabbits. (A) Periodically, the knees of all rabbits were lavaged with saline and the IL-1Ra content in recovered fluids measured by ELISA. Data are shown as the mean ± SD. For rabbits receiving scAAV-IL-1Ra, using a two-sample t-test and p < 0.05, no significant differences were observed between inflamed and normal knees for all days post-injection. The same test conducted for rabbits injected with saline showed no significant differences between normal and inflamed as well. (B) Infiltrating leukocytes in lavage fluids recovered at days 3 and 7 for each group were quantified using a hemocytometer. Data are shown as the mean ± SD. A pooled two-sample t-test was used to determine the significance of the differences in leukocytic infiltration in inflamed knees that were injected with scAAV.IL-1Ra and untreated controls. *p < 0.05.