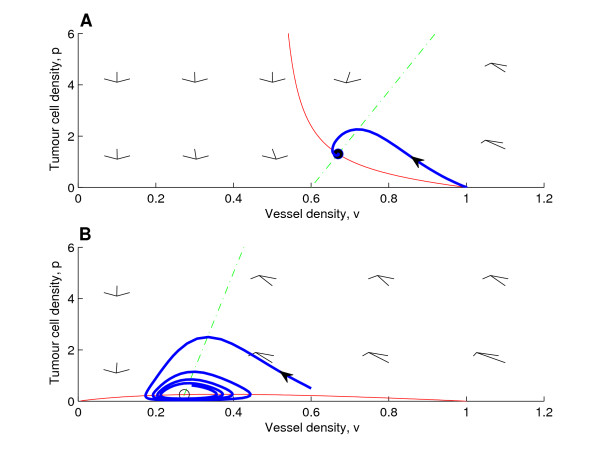
Figure 1.
Typical phase planes. (A) Typical phase plane with (non-zero) nullclines for case (a), here for δ/η0 < 1, showing a steady state which is a stable spiral. (B) Typical phase plane with (non-zero) nullclines for case (b), δ/η0 > 1. The steady state is unstable and the shown trajectory evolves into a stable limit cycle. We remark that compared to (A) we have varied δ, ds and σp (ds and σp were chosen so that the co-existence steady state would be unstable). Key: green dashed-dotted lines: non-zero p-nullclines; solid red lines: non-zero v-nullclines; open circle: linearly unstable steady state; closed circle: linearly stable steady state; blue bold lines with solid arrow: trajectories for the initial conditions (p(0), v(0)) = (0.01, 1) (A) and (p(0), v(0)) = (0.5, 0.6) (B). Parameter values: η0 = 0.02, dp = 0.8, ds = 0.9, δ = 0.01, sβ = 0.1 and σp = 0.08 (A) and η0 = 0.02, dp = 0.8, ds = 0.4, δ = 0.03, sβ = 0.1 and σp = 0.01 (B).