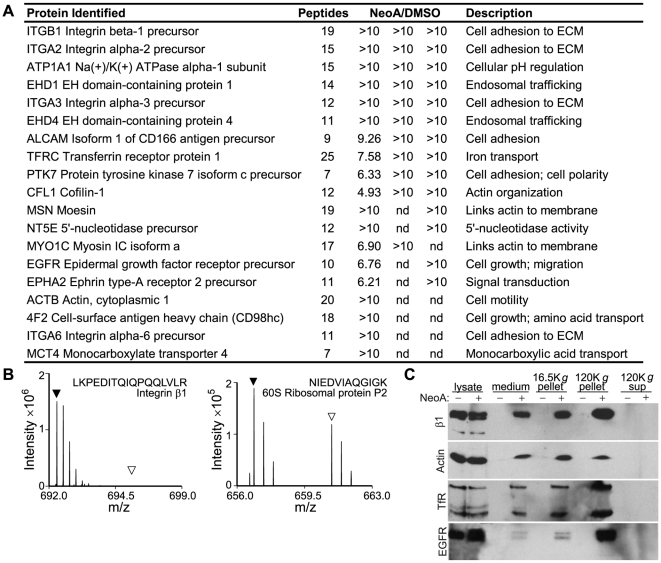
Figure 6. Characterization of released vesicles.
(A) List of the most abundant proteins (based on spectra counts) found preferentially in the NeoA-treated pellets versus DMSO-treated pellets from MDA-MB-231 cells. Ratios of peptides in NeoA vs. DMSO pellets (NeoA/DMSO) from each of three experimental replicates analyzed are listed. nd, not detected. (B) Representative mass spectra from proteomic analysis of the pellets from NeoA-treated (black triangles) and DMSO-treated (open triangles) cells. Triangles mark the position expected for the peptide. Spectra of a protein highly enriched in the pellet of NeoA-treated cells (left) and of a protein present at similar levels in the pellets from both NeoA-treated and DMSO-treated cells (right) are shown. (C) β1 integrin (β1), actin, transferrin receptor (TfR), and EGF receptor (EGFR) can all be detected in the conditioned medium from MDA-MB-231 cells treated with 13 µM NeoA and can be pelleted at high centrifugal speeds. On the gel, from DMSO (−) or NeoA (+) treated conditions: 5 µg of cell lysate; 50 µl of conditioned medium; 1/4 of pellet from 16,500 g spin; 1/4 of pellet from 120,000 g spin; 50 µl of supernatant from final spin. Note that, since pellets in this experiment were not re-suspended in the same volume as the supernatant they were pelleted from, comparisons of protein levels on this blot can only be made between the treated and control samples for each pellet or supernatant.