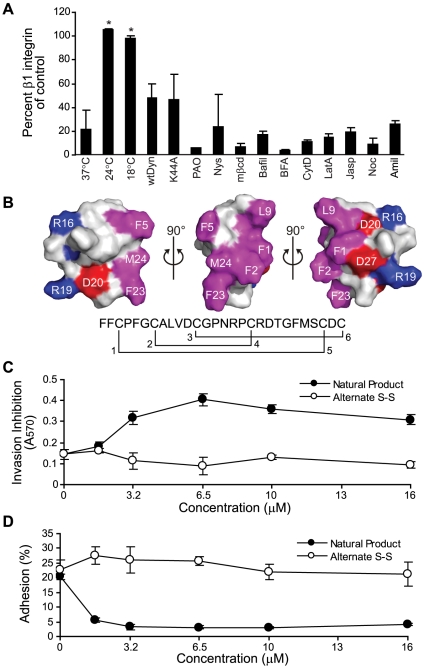
Figure 9. NeoA's effects are temperature sensitive and structure dependent.
(A) Percent β1 integrin levels (compared to untreated vehicle controls) on the cell surface of NeoA-treated cells under the indicated temperature conditions (i.e. 37°C or 24°C), or in the presence of the following inhibitors all at 37°C: wild-type dynamin control (wtDyn); dominant negative dynamin (K44A); phenylarsine oxide (PAO); nystatin (nys); methyl-β-cyclodextrin (mβcd); bafilomycin (Bafil); brefeldin A (BFA); cytochalasin D (CytD); latrunculin A (LatA); jasplakinolide (Jasp); nocodazole (Noc); or amiloride (Amil). Surface β1 integrin levels were measured by flow cytometry. Results are averages from two independent experiments. * P<0.05 compared to cells treated at 37°C as determined by two-tailed Student's t-test. (B) Surface representation of NeoA, with hydrophobic residues shown in magenta, whereas positively- and negatively-charged residues are in blue (Arg) and red (Asp), respectively. Note the large hydrophobic patch flanked by charged groups. MDA-MB-231 cells were assayed for (C) invasion and (D) adhesion after treatment with the natural NeoA peptide (Natural product) or a synthetic peptide with an alternate disulfide bond connectivity (Alternate S-S). Shown are averages of triplicates ± SD.