Fig. 1.
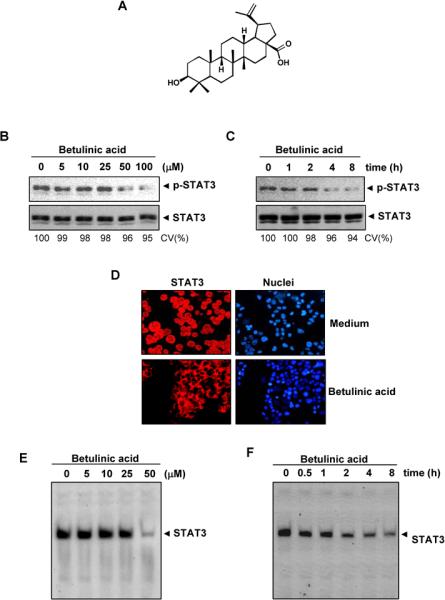
Effect of betulinic acid on constitutively active STAT3. A, The structure betulinic acid. B, Betulinic acid suppresses p-STAT3 levels. U266 cells (2 × 106/mL) were treated with the indicated concentrations of betulinic acid for 4 h, then whole-cell extracts were prepared, and 30 μg of protein was resolved on 7.5% SDS-PAGE gel, electro transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes, and probed for p-STAT3 C, Betulinic acid suppresses p-STAT3 levels in a time-dependent manner. U266 cells (2 × 106/mL) were treated with 50 μM betulinic acid for the indicated durations and analyzed for p-STAT3 levels. D, Betulinic acid causes inhibition of STAT3 translocation to the nucleus. U266 cells (1 × 105/mL) were incubated with or without 50 μM betulinic acid for 4 h and then analyzed for the intracellular distribution of STAT3 by immuno-cytochemistry. The same slides were counterstained for nuclei with Hoechst (50 ng/mL) for 5 min. E, Betulinic acid inhibits STAT3 DNA binding. U266 cells (2 × 106/mL) were treated with the indicated concentrations of betulinic acid for 4 h and analyzed for STAT3 DNA binding by EMSA. F, Cells were treated with 50 μM betulinic acid for the indicated durations and analyzed for nuclear STAT3 levels by EMSA. CV, cell viability
