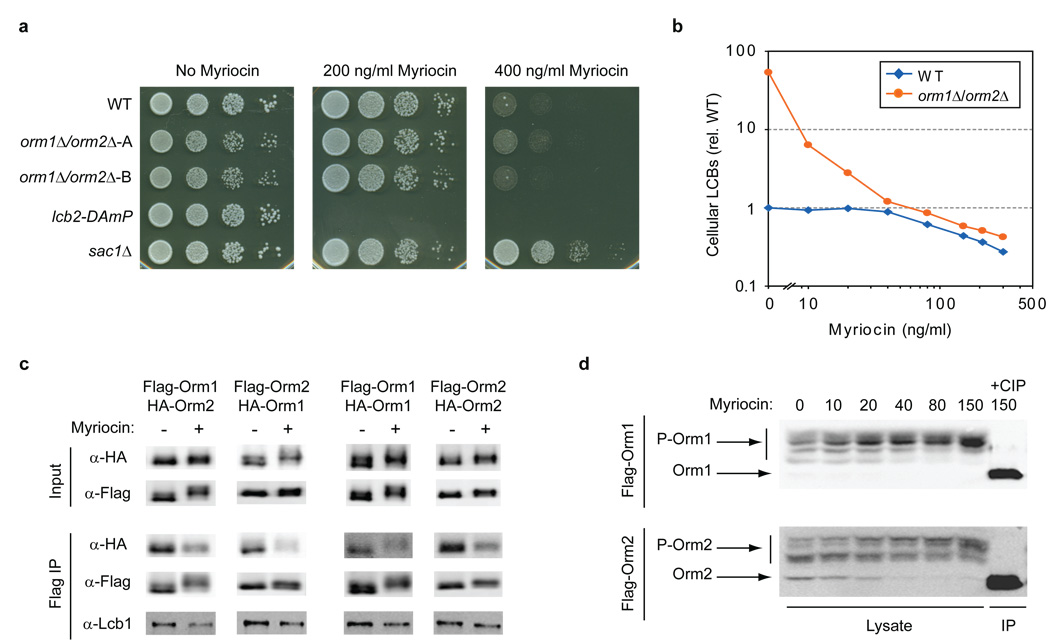
Figure 4. Orm1/2 are regulated in response to disruption of sphingolipid synthesis.
a, Serial dilutions of the indicated strains were spotted on plates with 0, 200, or 400 ng/ml myriocin and imaged after growth for 24–48 hr. b, LCBs were extracted and analyzed from wild-type (WT) and ORM1/2 deletion strains grown in media supplemented with the indicated concentrations of myriocin. The sums of C18 dihydrosphingosine and phytosphingosine peak intensities from n ≥ 2 experiments are shown (relative to wild-type LCB levels in the absence of myriocin). c, Native immunoprecipitations of 3×Flag-tagged Orm1 and Orm2 were performed from strains grown in standard media or media supplemented with 150 ng/ml myriocin and analyzed by Western blot. The indicated strains also expressed 3×HA-Orm1/2 from their endogenous loci (diploid strains were used to examine self-association of Orm1 and Orm2). d, Lysates were prepared from yeast expressing 3×Flag-Orm1/2 after growth in media containing the indicated concentrations of myriocin. Western blots show phosphorylated forms of 3×Flag-Orm1 (P-Orm1) and 3×Flag-Orm2 (P-Orm2) after separation on phosphate-affinity gels35. An immunoprecipitated (IP) sample treated with calf intestine phosphatase (CIP) shows the position of un-phosphorylated Orm1/2.