Figure 2.
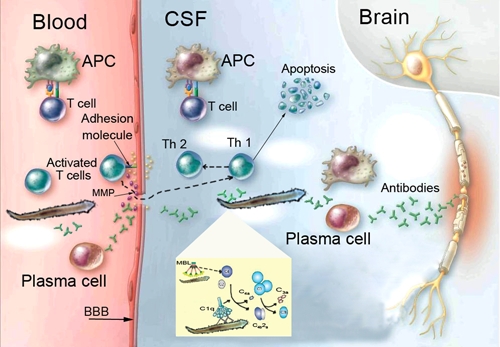
Mechanisms involved in the immune response and C4 intrathecal synthesis against Angiostrongylus cantonensis larvae invasion throughout the damaged blood-brain barrier (BBB). Larvae take advantage of existing factors such as metalloproteinases (MMPs) and adhesion molecules to enter the cerebrospinal fluid space. Antigen-presenting cells (APCs) are important in the innate response. C4 can play an essential role by the interaction with mannose-binding lectin (MBL) or C2 from the classical pathway. Complement component 2 bound to C4b is cleaved by classical (C1s) or lectin (MASP2) proteases to produce C4bC2a.The final products of complement activation forming the membrane attack complex with the interaction of Th1 and Th2 mechanisms produce inflammation, necrosis, and apoptotic cells. Neurotoxins produced by eosinophils during the inflammation process including antibody production should be the most responsible for the central nervous system damage. This figure appears in color at www.ajtmh.org.
