Figure 1.
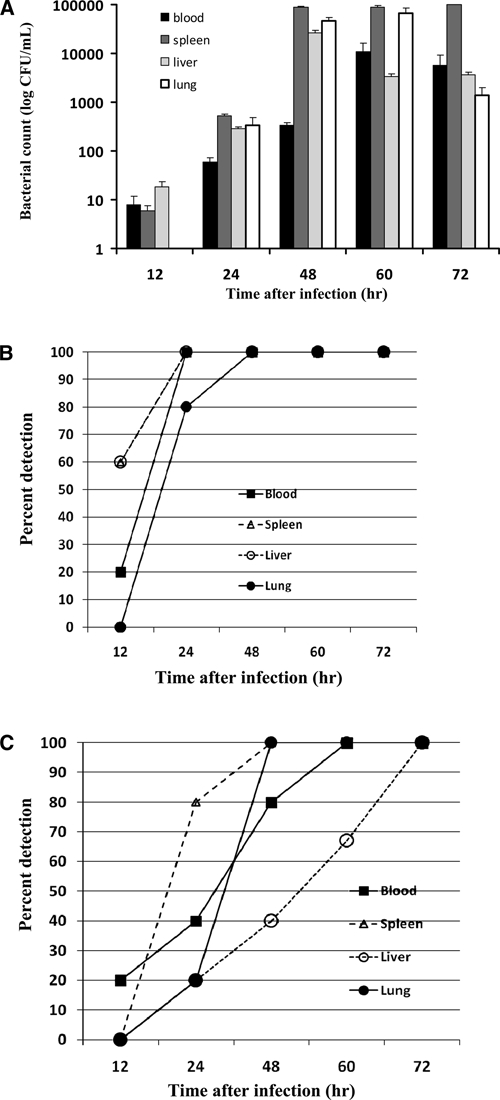
Kinetics of bacterial loads in blood and organs of high-dose Burkholderia pseudomallei-infected mice. Forty BALB/c mice were infected intraperitoneally with 12 50% lethal doses (230 colony-forming units) of B. pseudomallei A2. Mice were divided into 5 groups (8 mice/group). Groups 1–5 were infected with B. pseudomallei and their blood (black box), spleen (dark gray box), liver (light gray box), and lungs (white box) were collected after 12, 24, 48, 60, and 72 hours after infection. Mice were monitored for bacterial load by culture on Ashdown's selective medium and identified by using monoclonal antibodies (A). Each bar represents the logarithm of the mean ± SE colony-forming units. Control mice are not shown because no bacteria were detected in their blood samples. Percentage of positive results in blood and organs as detected by culture (B) or polymerase chain reaction (C) at various times after infections were plotted against time. Results were obtained from two independent experiments.
