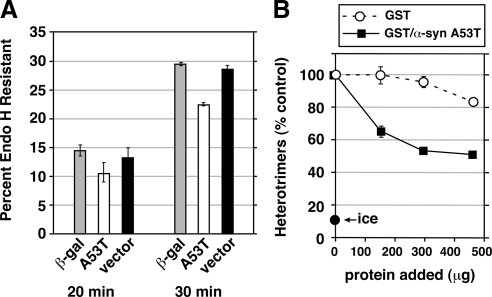
Figure 8.
(A) α-Synuclein inhibits transport before cargo modification by mannosidase II. NRK cells were electroporated with VSV-G-myc DNA together with a construct for either β-galactosidase, α-synuclein A53T, or pcDNA3.1 vector alone. After 24 h, the cells were infected with vaccinia virus vTF7 for 6 h at 40°C to amplify expression (see Materials and Methods). Cells were either lysed directly (data not shown) or shifted to 32°C for 20, 30, or 40 (data not shown) minutes before lysis, digestion with endoglycosidase H, and immunoblotting with anti-myc to detect VSV-G-myc. Histograms show GR as a percentage of GS + GR. Error bars show SE of duplicate gels run on the same cell extracts. The same trends were observed in a completely separate experiment with multiple time points. Supplemental Figure S4 shows one of the immunoblots from which the data were quantified. (B) α-Synuclein A53T directly inhibits COPII vesicle fusion to form pre-Golgi intermediates. Homotypic COPII vesicle fusion measured using the in vitro VSV-G heterotrimer cargo mixing assay. Purified proteins were added after vesicle budding and were incubated with the budded vesicles for 1 h before a 1 h fusion reaction at 32°C. “Ice” indicates heterotrimer signal obtained when the budded vesicles were mixed but left on ice during the fusion incubation. Fusion assay data are presented as means of duplicate determinations with error bars representing SE where larger than symbol size.