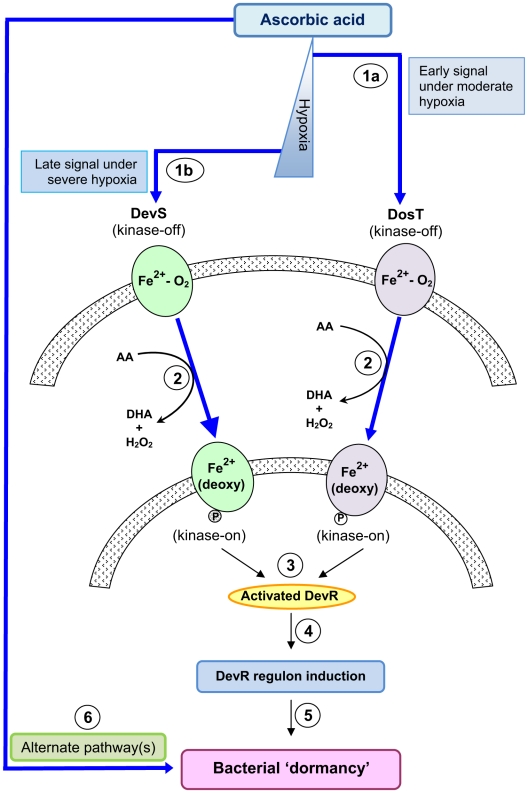
Figure 8. M. tb ‘dormancy’ response to ascorbic acid.
In one pathway, hypoxia generation by AA is sensed by DosT and DevS resulting in their activation (first deoxy-DosT and then deoxy-DevS under progressive hypoxia, steps 1a, 1b and 2). The transfer of phosphosignal from the sensors to DevR results in its activation (3). Activated DevR binds to target gene promoters and triggers DevR regulon mechanisms (4) and bacterial ‘dormancy’ (5). Bacterial ‘dormancy’ is also attained through alternate pathway(s) upon exposure to vitamin C (6).