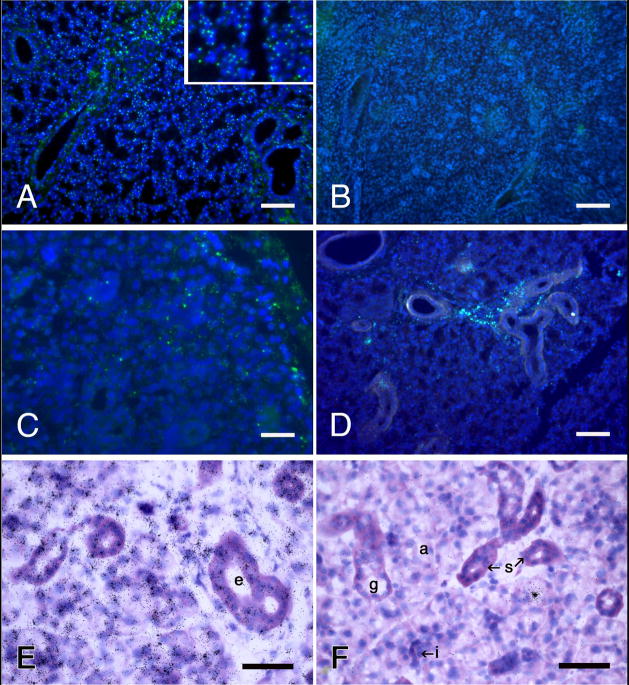
Fig. 2.
Identification of the Y-chromosome in rat submandibular glands by fluorescence in situ hybridization (A–D) and autoradiography of 35S-labeled antibodies to digoxygenin coupled to the probe (E, F). A, E, male controls; B, F, female controls; C, D, glands from female rats one hour and eight days, respectively, after being infused with dispersed cells from male rat submandibular glands. Y-chromosomes (small, bright yellow-green spots) are located in about 70% of the blue nuclei in A and none of the nuclei in B. Similarly, tight, radiating clusters of silver grains are atop the nuclei in E, and atop none in F. The lone cluster of grains in F is over the secretory granules of an acinar cell, illustrating a rare “false positive” artifact. E, F, basic fuchsin and toluidine blue stains. Scale bars = 100 μm (A, B and D), 25 μm (C), and 50 μm (E and F).