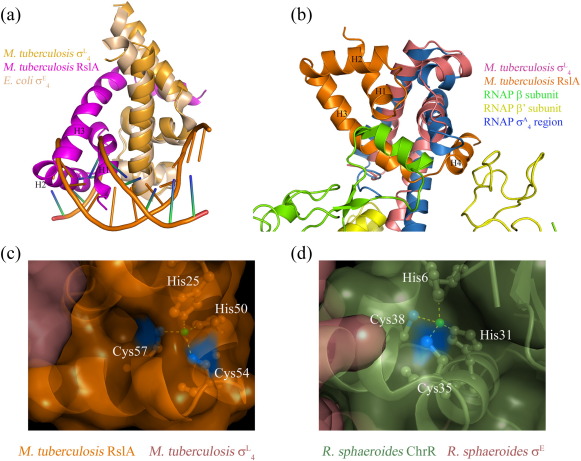
Supplementary Fig. 3.
(a) RslA sterically occludes the promoter recognition region of σ4L. The σ4L/RslA complex was superposed on the crystal structure of the σ4E/− 35 promoter DNA complex (PDB ID 2H27).20 (b) Docking of the σ4L/RslA complex onto Thermus thermophilus holo-RNAP (PDB ID 1IW7).22 Docking of RslA on polymerase reveals several steric clashes of RslA with a helical stretch of the β-subunit. (c) Surface representation of the region containing bound Zn2+ in the ASDs of RslA and ChrR. The sulfur atoms of the cysteine residues (Zn2+ binding) are shown in blue. Both cysteines in the CXXC motif in Mtb RslA are accessible to the solvent. The solvent-accessible cysteines in Mtb RslA provide a structural rationale for the redox sensitivity of this ASD. (d) A surface representation of Rsp ChrR in a similar orientation as Mtb RslA in (c). The Cys38 of the CXXC motif is occluded by Arg41 (Rsp ChrR numbering).