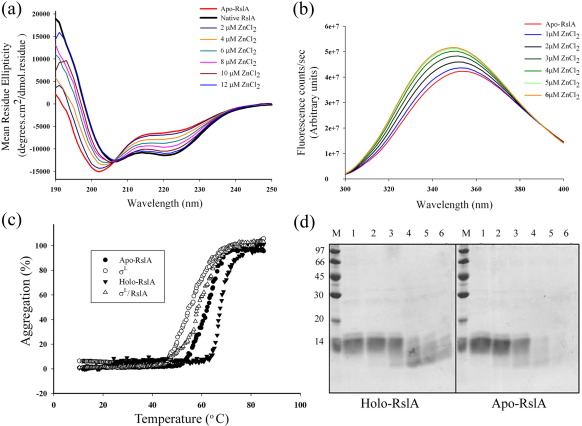
Fig. 3.
Zinc removal with an oxidative stimulus induces conformational changes in RslA and in the σL/RslA complex. (a) CD spectra showing changes in the secondary structure of RslA with increasing concentration of Zn2+ under reducing conditions. (b) Zinc binding monitored by intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence. Zinc binding stabilizes helix H1 of RslA. (c) Zinc binding confers stability to RslA and the σL/RslA complex. Temperature-induced denaturation of σL, RslA, and the σL/RslA complex. As seen by thermal melting profiles, Zn2+ binding confers stability to RslA and the σL/RslA complex. Temperature was scanned between 10 °C and 90 °C, with a dT/dt of 1 °C/min. (d) Zn binding does not confer significant resistance to RslA proteolysis. In this experiment, holo-RslA and apo-RslA were incubated with trypsin (1:2000) for various time points and analyzed on 12% SDS-PAGE. Lane 1, 0 min; lane 2, 5 min; lane 3, 10 min; lane 4, 20 min; lane 5, 30 min; lane 6, 60 min.