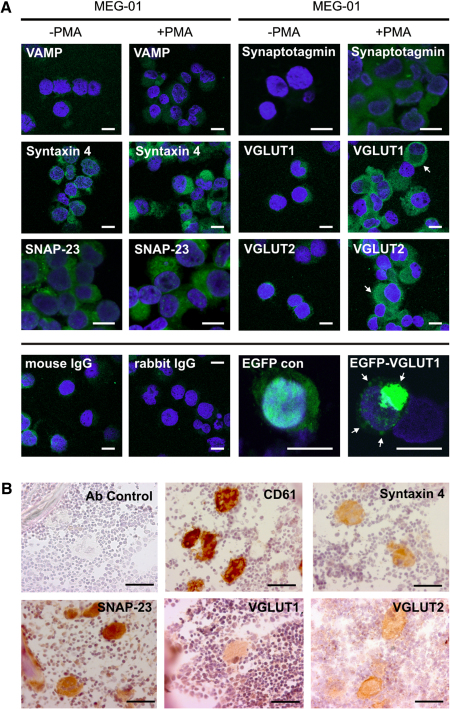
Figure 3.
Immunolocalization of soluble N-ethyl maleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) complex and accessory proteins in megakaryocytes. (A) Immunofluorescent localization of SNARE complex and accessory proteins (green) was determined by confocal laser scanning microscopy in MEG-01 cells in the undifferentiated (−phorbol myristate acetate [PMA]) as well as differentiated (+PMA) state, nuclei were stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (blue); the bottom row shows negative controls for vesicle-associated membrane protein (VAMP) and Syntaxin (mouse immunoglobulin G) and for Synaptotagmin, SNAP-23, vesicular glutamate transporter (VGLUT) 1, and VGLUT2 (rabbit immunoglobulin G) immunostainings, as well as the overexpression of enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP)-VGLUT1 in undifferentiated (−PMA) MEG-01 cells and empty vector control (EGFP con); arrows indicate elevated accumulation of VGLUT1 and VGLUT2 at the cell periphery in differentiated MEG-01 cells as well as dense distribution of VGLUT1 in specific regions near the plasma membrane of VGLUT1-transfected cells; bar = 20 μm. (B) Brown staining reports expression of SNARE complex proteins (Syntaxin 4 and SNAP-23) and VGLUT1/2, respectively, in rat bone marrow. Detection of CD61 was used to confirm megakaryocyte identity. Nuclei were counterstained with hematoxylin (blue); bar = 30 μm.