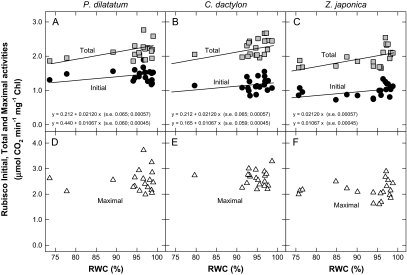
Fig. 1.
Rubisco initial, total and maximal carboxylation activities (μmol CO2 min−1 mg−1 chlorophyll) as a function of the relative water content (RWC, %) in the leaves of Paspalum dilatatum (A, D), Cynodon dactylon (B, E), and Zoysia japonica (C, F). Initial activities (A–C, black symbols) were determined immediately after extraction, total activities (A–C, grey symbols) after activation in the presence of CO2 and Mg2+, and maximal activities (D–F, open symbols) after removal of tight-binding inhibitors with sulphate. Each data point corresponds to one sample, with seven (P. dilatatum and Z. japonica) or eight (C. dactylon) control (well-watered) and 12 non-watered samples per species. Regression lines were fitted when the RWC effect was significant (F-test; Initials: R2=50.5%, s2=0.033, df=55, P <0.001; Totals: R2=32.5%, s2=0.052, df=56, P <0.001; Maximals: no regression on RWC, P >0.05).