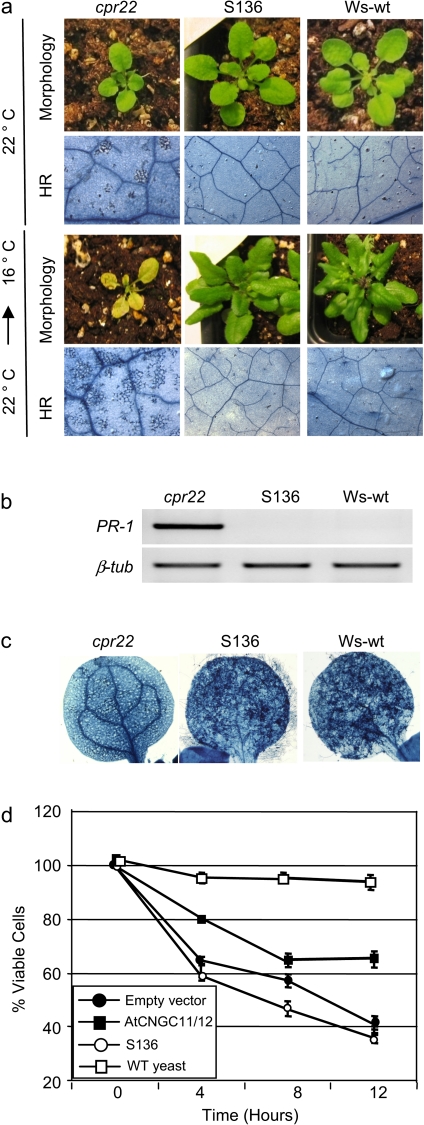
Fig. 7.
Characterization of the premature stop codon mutant, S136. (a) Morphological and cell death phenotypes of Ws-wt, cpr22 and S136 with and without temperature shift. S136, unlike S58 does not induce cell death after a shift from 22 °C to 16 °C. Samples were taken 7 d after the shift. (b) RT-PCR analysis for PR-1 gene expression in Ws-wt, cpr22, and S136. The samples were taken from approximately 4-week-old plants. β-tublin (β-tub) served as a loading control. (c) Growth of Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis, isolate Emwa1 in Ws-wt, cpr22, and S136. Plants were infected by spraying a conidiospore suspension of 106 ml−1 on 7-d-old plants. The Trypan blue analysis 8 d after infection was done to visualize pathogen growth. (d) Yeast complementation analysis using the Ca2+-uptake deficient mutant K927. Only AtCNGC11/12 but not S136 (AtCNGC11/12: Q543X) rescued the K927 phenotype. Data are the average of three biological repeats ±SE. Student's t test shows a significant difference between AtCNGC11/12 and both empty vector and S136 at 12 h (P <0.05).The experiment has been repeated more than three times with similar results.