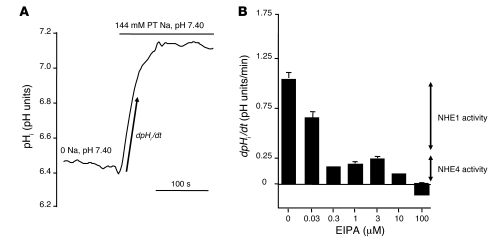
Figure 3. Measurement of basolateral Na+/H+ exchange activity in rat MTALH cells.
Tubules were initially perfused and bathed with a Na+-free, CO2/HCO3–-free, HEPES-buffered solution (solution A). Luminal fluid also contained 0.1 mM furosemide and 1 mM amiloride to prevent apical Na+ entry and proton efflux. After a 2-minute recording, the peritubular (PT) solution was changed to a 144 mM Na+, CO2/HCO3–-free, HEPES-buffered solution (solution B), containing EIPA at various concentrations. The initial rate of pHi recovery (dpHi/dt) was calculated on the linear part of the curve after peritubular Na+ addition. (A) The effect on pHi of peritubular Na+ addition under control conditions. The figure shows an example of the pHi time course, before and after Na+ addition. The arrow shows the initial, linear change in pHi, allowing the calculation of dpHi/dt. In the absence of external Na+, pHi was close to 6.4 and was identical in all experiments regardless to the EIPA concentration. (B) The effect of various peritubular concentrations of EIPA on Na+/H+ exchange activity in the rat MTALH. The inhibition elicited by the various concentrations of EIPA was consistent with the presence of 2 components of Na+/H+ exchange activity with distinct EIPA sensitivities: 0.3 to 3 μM EIPA inhibited approximately 80% of the initial rate of pHi recovery, corresponding to NHE1 activity; 100 μM EIPA was required to completely inhibit pHi recovery (NHE1 and NHE4 activities, shown by arrows).