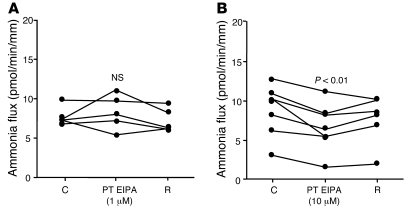
Figure 4. Effect of peritubular EIPA on transepithelial ammonia absorption in the rat MTALH.
(A) The effect of 1 μM peritubular EIPA. Tubules were perfused and bathed with a standard solution, containing 139 mM Na+ and 4 mM NH4+ (solution C). The addition of 1 μM EIPA to the peritubular solution had no effect on Vte (Vte: control [C], 12.1 ± 1.6 mV; 1 μM EIPA, 12.7 ± 1.3 mV; recovery [R], 11.8 ± 1.9 mV; NS; flow rate: control, 3.2 ± 0.4 nl/min; 1 μM EIPA, 3.1 ± 0.3 nl/min; recovery, 3.1 ± 0.3 nl/min; NS) or transepithelial ammonia flux. Individual results obtained with 5 independent tubules are displayed. (B) The effect of 10 μM peritubular EIPA. Addition of 10 μM EIPA to the peritubular solution elicited a decrease in transepithelial ammonia flux. Vte and flow rate were not affected by EIPA (Vte: control, 7.9 ± 1.4 mV; 10 μM EIPA, 9.2 ± 1.4 mV; recovery, 8.7 ± 1.2 mV; NS; flow rate: control, 3.0 ± 0.2 nl/min; 10 μM EIPA, 3.1 ± 0.2 nl/min; recovery, 3.8 ± 0.3 nl/min; NS). Individual results obtained with 7 independent tubules are displayed.