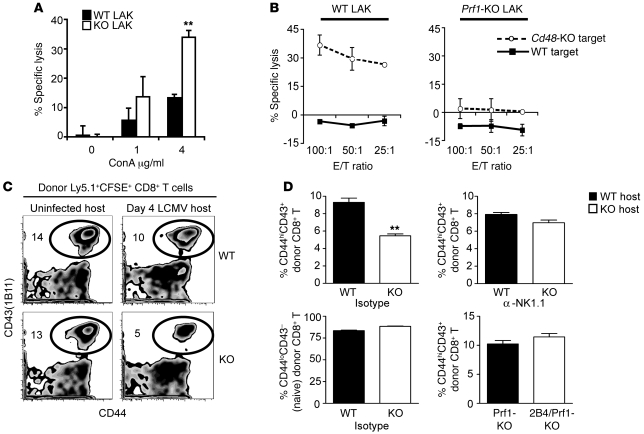
Figure 8. NK cells mediate specific lysis of activated CD8+ T cells in the absence of 2B4 in vitro and in vivo.
(A) WT (black bars) or 2B4-KO (white bars) LAK cell killing (mean ± SD) of WT CD8+ T cell targets, activated in vitro with various doses of ConA. (B) Specific lysis (mean ± SD) of WT or CD48-KO ConA-activated CD8+ T cells by WT (left) or by Prf1-KO (right) LAK cells is shown at various effector to target (E/T) ratios. (C and D) A modified in vivo cytotoxicity assay was done by injecting CFSE-labeled splenocytes (3 × 107) from LCMV-infected (day 4 p.i.) congenic (Ly5.1+) WT mice into uninfected or LCMV-infected (day 4 p.i.) WT and 2B4-KO mice (Ly5.2+, n = 5–6/group), some of which were depleted of NK cells 1 day prior to infection. Five hours after transfer, the proportion of activated (CD44hiCD43[1B11]+) donor (Ly5.1+CFSE+) cells was determined in each mouse. (C) Representative CD44 and CD43(1B11) expression by donor Ly5.1+CFSE+ CD8+ T cells. Numbers are the percentage of donor (Ly5.1+CFSE+) CD8+ T cells that are CD44hiCD43(1B11)+ for the representative sample shown. (D) Top graphs depict the percentage of activated CD44hiCD43(1B11)+ donor (Ly5.1+CFSE+) CD8+ T cells in isotype- (left) or anti-NK1.1–treated (right) WT and 2B4-KO mice. Lower left plot demonstrates the proportion of naive phenotype (CD44loCD43[1B11]–) donor (Ly5.1+CFSE+) CD8+ T cells in isotype-treated WT and 2B4-KO mice. Lower right plot depicts the percentage of activated CD44hiCD43(1B11)+ donor (Ly5.1+CFSE+) CD8+ T cells in Prf1-KO and 2B4/Prf1-KO mice. Results are presented as mean ± SD. **P < 0.01 (2-tailed unpaired Student’s t test). Data are from 1 of 3 similar experiments.