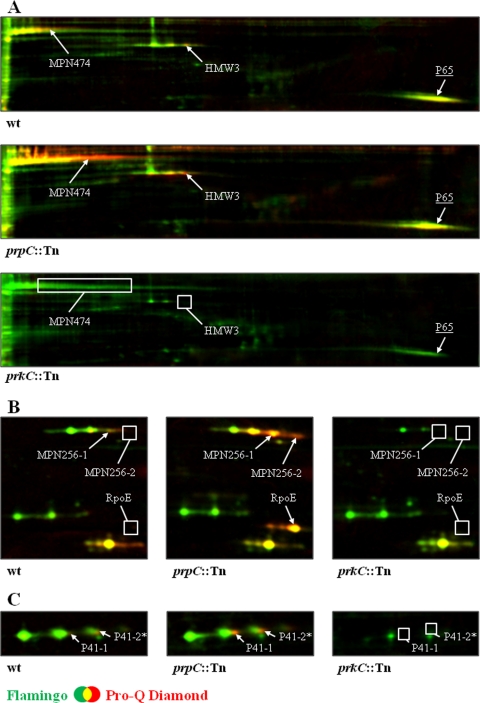
Fig. 2.
PrpC/PrkC-dependent modification of cytadherence proteins in M. pneumoniae Shown are sections of dual channel images of Flamingo fluorescent dye- (green) and Pro-Q Diamond-stained (red) two-dimensional gels representing selected proteins in the M. pneumoniae wild type, prpC::Tn mutant, and prkC::Tn mutant. Proteins were separated on an 18-cm IPG strip with a linear pH gradient of pI 4.5–5.5 in the first dimension. The proteins HMW3, MPN474, P65 (A), MPN256, RpoE (B), and P41 (C) are shown. Putative phosphorylated proteins in the M. pneumoniae wild type as well as proteins with increased or new phosphorylation spots in the prpC::Tn mutant are indicated. Missing phosphorylation spots in the M. pneumoniae wild type and the prkC::Tn mutant are highlighted by a box. Protein amounts of HMW3, MPN256, and P41 (all represented by a triple protein spot) seem to be reduced as well as for the P65 protein (underlined) in the prkC::Tn mutant. Note that the P41 spot “2*” is only putative because of a low Pro-Q Diamond/Flamingo log ratio in the analyzed strains. Protein spots were cut from the gel and identified by MS/MS (see Table I and supplemental Table S3).