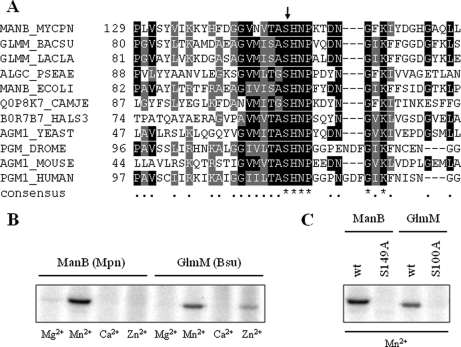
Fig. 6.
Autophosphorylation on universally conserved serine residue in active site of phosphosugar mutases. A, multiple alignment of the conserved phosphoserine signature of phosphosugar mutases from all domains of life. Amino acids with similarities in at least two of the sequences are highlighted in gray, whereas amino acids that are identical in at least two of the sequences are depicted in a black background. The UniProtKB entry names of the aligned sequences are MANB_MYCPN (ManB, M. pneumoniae), GLMM_BACSU (GlmM; B. subtilis), GLMM_LACLA (GlmM; L. lactis), ALGC_PSEAE (AlgC; P. aeruginosa), MANB_ECOLI (ManB; E. coli), Q0P8K7_CAMJE (ManB; C. jejuni), B0R7B7_HALS3 (PMM1; H. salinarum), AGM1_YEAST (AGM1; Saccharomyces cerevisiae), PGM_DROME (PGM; D. melanogaster), AGM1_MOUSE (AGM1; Mus musculus), and PGM1_HUMAN (PGM1; Homo sapiens). The conserved active site phosphoserine is indicated by an arrow. B, M. pneumoniae ManB and B. subtilis GlmM autophosphorylation assay in the presence of various divalent cations. About 5 μg of purified His-tagged ManB (lanes 1–4) or GlmM (lanes 4–8) were incubated in the presence of [γ32P]ATP in an autophosphorylation assay (see “Experimental Procedures”). Each reaction mixture was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and phosphorimaging analysis. Divalent cations (5 mm) used in the assays are indicated below the lanes. Bsu, B. subtilis; Mpn, M. pneumoniae. C, autophosphorylation assay of M. pneumoniae ManB (wild type (wt) and S149A) and B. subtilis GlmM (wild type and S100A) recombinant proteins. The four recombinant proteins were checked for autophosphorylation as described in B. Autophosphorylation reactions were conducted in the presence of Mn2+ (5 mm) as divalent cation as it showed the strongest signal in B.