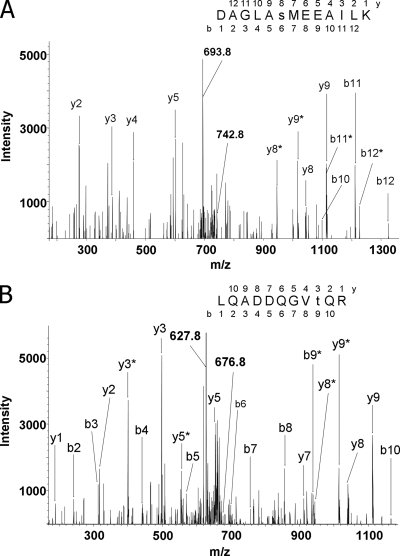
Fig. 3.
Mass spectrometric sequencing of phosphorylated peptides from Stt7 and Stl1 protein kinases. Peptides were obtained by tryptic cleavage of isolated thylakoid membranes of the wild-type C. reinhardtii cells exposed to state 2 conditions. Peptides were then methylated and subjected to IMAC enrichment of phosphopeptides. The collision-induced fragmentation spectra of the peptides are shown. The b (N-terminal) and y (C-terminal) fragment ions are labeled in the spectra and in the displayed peptide sequences, which were deduced from the spectra. Lowercase s and t in the sequences designate phosphorylated serine and threonine residues, respectively. Fragment ions that contained a phosphorylated residue and underwent the neutral loss of phosphoric acid (H3PO4; mass, 98 Da) are marked with asterisks. Phosphorylation sites were localized according to the pattern of the fragment ions containing phosphate and corresponding fragments with the neutral loss. A, the fragmentation spectrum of the doubly protonated peptide ion with m/z = 742.8 (indicated). The peptide corresponds to amino acids 528–540 from Stt7 protein. The doubly charged ion indicated at m/z = 693.8 corresponds to the parent ion after the neutral loss of phosphoric acid (742.8 × 2 − 693.8 × 2 = 98). Phosphorylation of the serine residue is evident from the distinct set of the fragment ions: y8, y8*, and y5. B, the fragmentation spectrum of the doubly protonated peptide ion with m/z = 676.8 (marked). The peptide corresponds to amino acids 159–169 from Stl1 protein. The doubly charged ion indicated at m/z = 627.8 corresponds to the peptide with the neutral loss of phosphoric acid. The site of phosphorylation has been localized according to the pattern of the ions containing phosphate and the satellite fragments with the neutral loss of phosphoric acid: y3, y3*, b8, and b9*.