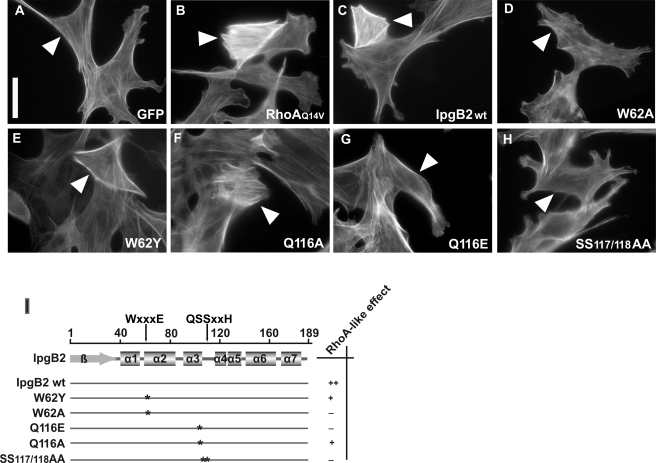
FIGURE 4.
Biological activity of IpgB2 and verification of critical residues in the putative catalytic loop. A–H, fibroblast cells expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) alone (negative control), GFP-tagged constitutively active RhoAQ14V (positive control), wild-type IpgB2, and different point mutants as indicated were fixed and stained for the actin cytoskeleton. Transfected cells are marked by white arrowheads (compare also with supplemental Fig. 1). RhoA and wild-type IpgB2 strongly induced the formation of parallel actin stress fibers. IpgB2 mutants displayed no (D, G, and H) or moderate (E and F) biological activity. The bar equals 25 μm. I, schematic overview and summary of the IpgB2 mutants studied. Of note, the biological activity of none of the mutants was as strong as that seen with wild-type IpgB2, which caused effects virtually identical to RhoAQ14V already at low expression levels of the construct, as judged by GFP fluorescence (see also supplemental Fig. 1) (categorized as strong, ++). Mutants that lacked any notable activity even at high expression levels were classified as negative (−), whereas the responses observed with positive mutants were generally more variable than wild type and required strong overexpression to induce wild-type-like effects (categorized moderate, +). At least 25 individual cells were categorized for each construct.